
What Is Attack Surface Management, And Why Is It Important?
October 21, 2022
WonderCMS 3.1.3 Vulnerable to Authenticated Server-Side Request Forgery – CVE-2020-35313
November 9, 2022
Ransomeware attacks are increasingly becoming a growing concern over the past few years. As remote work is becoming the new normal amongst numerous industries worldwide, ransomware operators are actively devising new means to target online vulnerabilities and extort unsuspecting companies.
As a part of our ongoing Cyber Awareness Month series dedicated to spreading the importance of online security, we wanted to shed light on what is a ransomware attack and provide readers strategic tips on how you can actively protect yourself against them.
What is a ransomware attack?
Ransomware is a form of malware that hackers leverage to take control of victim accounts and sensitive data. These bad actors threaten victims to cut off access or publicize the data unless they duly pay a ransom.
The extremes of malware attacks vary where some demand payment for account access while others outrightly extort victims with private data to obtain a large payday illegally.
Why are ransomware attacks so common?
Ransomware attacks are becoming more frequent because organizations and individuals often prefer to pay the ransom rather than combat the attack.
The reasoning is that they feel it’s cheaper and easier to rid themselves of their predicament than go through the tedious and expensive process of regaining access to their accounts and data. Most also feel it’s a less risky option to pay than suffer the pitfalls of a public data compromise.
The problem behind this approach is that it contributes to the success rate of ransomware attacks and encourages malicious actors to innovate the malware further and increase the scale of its utilization.
Some examples of companies compromised by ransomware
Ransomware attacks affect not only individuals and SMEs but also large corporations. Let us dive into some of the most notable ransomware attacks that caused severe damage to leading companies.
Acer
On March 14, 2021, the multinational Taiwanese advanced electronics and hardware giant Acer suffered a massive data breach where attackers demanded a sizable ransom of USD$50 million.
The infamous hacker group REvil exploited an undetected vulnerability in the company’s Microsoft Exchange server and gained access to several sensitive images, documents, and data.
Although Acer duly paid the ransom to avoid further damage, they never recovered the data from REvil.
Brenntag
After suffering a ransomware attack, the German chemical distribution company Brenntag negotiated down from the initial USD$ 7.5 million ask by the group DarkSide and ultimately paid USD$4.4 million in bitcoin to regain roughly 150GB of stolen data.
The sensitive information consisted of severe leaks from the company’s finance, accounting, marketing, and legal departments, along with sensitive information about ongoing contracts, projects, and NDAs.
CNA
The Chicago-based financial corporation CNA got attacked by the Phoenix ransomware group in March 2021. This group gained access and encrypted around fifteen thousand CNA devices through server vulnerabilities.
The demand from the hacker group was USD$40 million, which CNA reportedly paid to regain access to their network.
Quanta
Industrial infrastructure company Quanta services suffered a highly publicized attack from REvil, the same attack group that breached Acer in 2021.
REvil, recognizing Quanta for being a certified Apple Inc. supplier, hacked and stole sensitive information on the Macbook’s schematics, components, and diagrams.
The group demanded Quanta and Apple Inc. a ransom of USD$50 million, which both companies declined to pay, leading to the hackers publicly leaking the sensitive information online.
CD Projekt
The Polish video game developer behind globally recognized game titles such as Cyberpunk 2077 and The Witcher suffered a major ransomware attack on February 2021.
The attackers reportedly compromised employee data, internal company reports, and the source codes of a few of their flagship games.
Rather than conform to the ransomware demands, the Polish company is working closely with authorities to bring the hacker group to justice.
How do ransomware attacks work?
First and foremost, the success of any ransomware attack depends on the ability of the malicious group to breach company systems, gain access and encrypt their files.
Typically, the next step is to claim responsibility for the attack through anonymous pseudonyms, furbish proof of data possession, and ultimately relaying their demands.
Although hackers employ numerous ransomware variants and methodologies to carry out these attacks, they generally follow a similar pattern.
Let us dive into the known ransomware stages and what it takes for hackers to launch a successful ransomware attack.
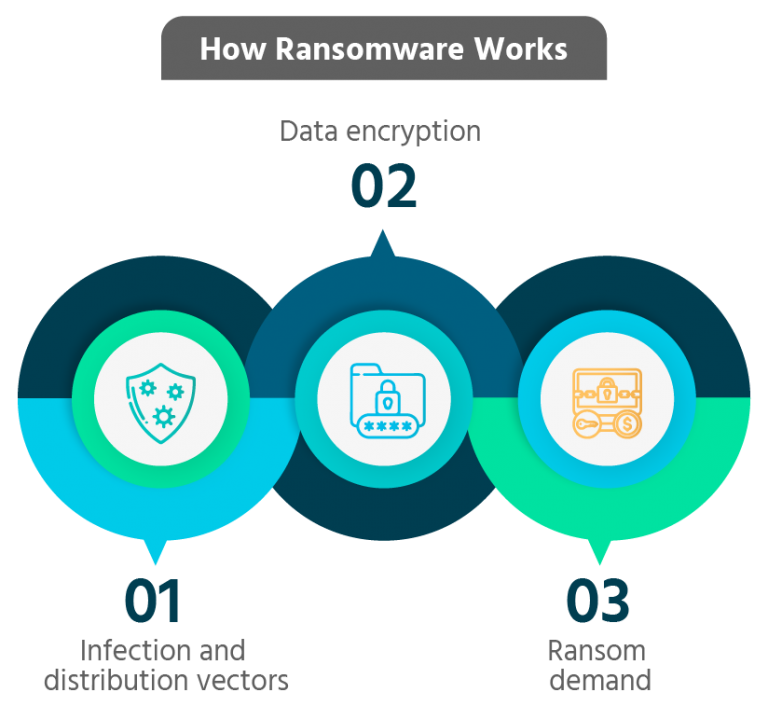
Step 1: Infection and distribution vectors
Infection attack vectors generally vary in how they breach the system. They sometimes use stolen employee credentials to gain remote access by exploiting the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) service.
During bolder instances, ransomware attackers have directly attacked the company network itself.
Another infection methodology is pushing the malware through a hyperlink disguised as a harmless email targeting employees.
Step 2: Data encryption
Once the attacker succeeds with a chosen attack vector and gains access to the company’s systems, their next step is encrypting the stolen data to cut off access to the victim. This process involves assigning an encryption key to the data known only to the ransomware perpetrators.
A more severe action that some attackers perform during this stage is an attempt to delete all known backups of the stolen data to increase its value and likelihood of achieving a quick payday.
Step 3: Ransom demand
The next step in the meticulous ransomware attack is to execute the ransom demand. It is common for attackers to first send a preview of the stolen data to companies to show the severity and business ramifications of a potential leak accompanied by an untraceable ransom note with financial demands.
It is also common practice for the ransom attacker to demand payment through cryptocurrency, making it almost impossible to track the funds or the receiver after the fund transfer.
In most cases, once the ransom is paid, the attackers release the decryption key to the company to recover their data.
However, there is no guarantee that the hackers may honor their end after receiving the ransom, as nothing is stopping them from going ahead and leaking the data.
Popular ransomware variants
Due to the effectiveness of this form of cybercrime, numerous new malware are developed by hackers every day.
Amongst the growing list, some stand apart as more dangerous than others due to their effective results and ability to dodge even the most adept ransomware detection tools.
Ryuk

This email phishing-based attack delivers a trojan horse or Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) onto the victim’s system that remains hidden inside the company network. While it lies undetected, it records user keystrokes and sensitive data on the host system.
As the hacker gains access to the broader network, the malware infects all other vulnerable network computers. While doing so, the APT may manipulate user rights to gain administrator access to begin data encryption.
This capability of Ryuk makes it one of the most feared ransomware malware variants present today.
Maze

This variant uses exploit kits, RDP, and email phishing to infiltrate unsuspecting networks to transmit stolen data onto private servers before being detected by the organization.
In some extreme instances, hackers using the Maze variant delete backups of the stolen data from the company servers.
REvil
One of the most popular variants, REvil, being pushed globally as ransomware as a Service (RaaS), has been the culprit behind numerous high-profile ransomware attacks.
REvil uses exploit kits, backdoors, and RDP servers to exfiltrate sensitive company data onto private servers.
Recently, the previously anonymous group behind REvil has reportedly been apprehended by authorities in Russia for their involvement in ransomware crimes against several businesses worldwide.
Lockbit

The Lockbit ransomware variant is known to gain access, encrypt business systems, and lock them out completely. It only provides businesses access to their systems after paying the ransom demands.
The idea behind Lockbit attacks is that businesses will suffer operational disruptions and data leaks by delaying or not paying the ransom.
It is also an infectious variant that can spread throughout the network on its own to target strategic locations for absolute system control.
Lockbit commonly uses social engineering and vulnerabilities in network configurations as a tactic to infiltrate systems and gain access.
Dearcry

The Dearcry malware variant exploits Microsoft exchange servers through its ProxyLogin vulnerabilities to infiltrate and disguise itself as a windows system service. It then collects all the information it needs to carry out the ransomware attack.
How to keep your organization protected from ransomware attacks
Keeping up with current trends in malware attacks and employing the best cyber security practices for your organization should be a fundamental priority to safeguard your business from emerging ransomware threats.
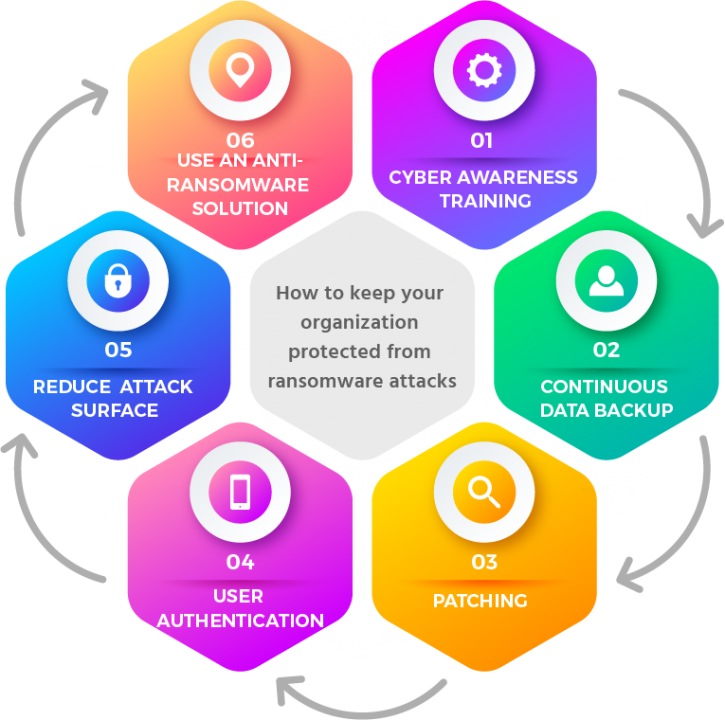
To help you further protect yourself, we have compiled a few best practices to follow.
1. Cyber awareness training
One of the most common entryways for ransomware breaches in enterprise systems is their employees. If you feel you haven’t adequately provided your employees with the knowledge necessary to safeguard themselves from cyber attacks, you must take action immediately.
This cyber awareness month is an opportune starting point to train employees and external stakeholders who have access to your network on the perils of ransomware attacks and how to prevent them from happening.
Some of the critical points you must address are how they can identify and protect themselves from email phishing and social engineering.
2. Continuous data backup
The worst byproduct of ransomware attacks is the operational delays you incur when you lose access to your systems and data until you pay off the attacker.
A simple yet effective solution to mitigate this is practicing continuous data backups, preferably situated off-network. These backups allow you to keep your business functioning while resolving the attack.
In such instances, even if the hacker deletes the data from the company network, it is still recoverable via external backups.
3. Patching
Cyber security experts spend countless hours identifying and resolving software vulnerabilities and rolling them out to businesses as patches. Without these patches, companies will remain highly vulnerable to ransomware attacks.
Always ensure that your systems are up-to-date with the latest software patches and updates to reduce the likelihood of potential breaches.
4. User authentication
Ransomware operators use social engineering and attack RDPs to acquire sensitive employee credentials.
To make this task significantly more challenging for them, empower your user authentication by strengthening passwords and deploying Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all stakeholders with enterprise network access.
These safeguards are excellent means to deny unrecognized authentication and stop attackers in their tracks.
5. Reduce attack surface
You significantly reduce your attack surface by actively addressing issues such as phishing, system weak spots, cross-platform malware, and remote access systems.
The best preventative measure businesses can take to protect themselves from being attacked is to make themselves an undesirable target for ransomware operators. By making yourself a difficult cyber target, ransomware attackers looking for a quick payday may not wish to burn their time and resources to scour your security perimeter for weaknesses.
Attacking a business with a reduced attack surface may be perceived as a futile attempt by some cyber criminals.
6. Use an anti-ransomware solution
Anti-ransomware or antivirus solutions aim to stay updated with active safeguards for existing and new threats.
Whenever the cyber security industry witnesses a unique ransomware fingerprint, experts swiftly attempt to analyze and devise quick means to identify and block the infection.
Excellent anti-ransomware solutions should allow you to detect and block a comprehensive list of variants quickly.
During instances where the infection makes it through to the network, their ransomware removal tools should be able to automatically remove the malware and then repair and restore the systems to normal.
However, these are just a few basic steps to help stop ransomware attacks. There is still a need for constant vigilance to ensure that you aren’t susceptible to ransomware attacks and can defend against any malware that finds its way into your network infrastructure.
That’s why even the most adept anti-ransomware solution isn’t enough, and the undeniable necessity for penetration testing is vital.
Secure your enterprise with continuous penetration testing
Continuous penetration testing helps the organization’s IT and security department learn how to detect and tackle breaches from intruders and protect the business from malicious actors.
Since ransomware operators are constantly growing in sophistication with their attack methodologies, regularly administering penetration tests helps businesses stay effectively safeguarded.
PTAAS companies provide the latest tools and updated penetration tests to help enterprises stay one step ahead of intruders with the latest safeguards.
Securelayer7 is a leading penetration testing partner that offers numerous enterprises state-of-the-art web apps, mobile apps, and cloud penetration testing to effectively safeguard themselves and their data from imminent security threats.
Contact us to find out how Securelayer7 can help fortify your organization’s cybersecurity by identifying and blocking ransomware variants from infecting your networks.