
Server-side Request Forgery (SSRF) via DNS Rebinding Attack
April 25, 2023
DevSecOps: A Guide For The Beginners
April 27, 2023
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is more important than ever. Businesses and organizations are constantly at risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to have a robust security protocol that includes both vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.

While both vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are important security measures, they serve different purposes and provide different types of information.
Vulnerability scanning is a process of identifying vulnerabilities in your system, while penetration testing is a more comprehensive approach that involves simulating a real-world attack to identify weaknesses in your system’s security.
In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between vulnerability assessment vs penetration testing, their respective benefits and limitations, and how they can be used together to create a comprehensive security strategy.
We’ll also discuss the factors to consider when deciding which approach is right for your organization and highlight the importance of engaging with a reputable and experienced cybersecurity provider to ensure the effectiveness of your security measures.
Pentesting vs Vulnerability Scanning
Let us delve deeper into the concepts of pentesting vs vulnerability scanning and learn more about them.
What is vulnerability scanning?
Vulnerability scanning is a process that involves scanning your system for known vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
It’s typically an automated process that uses software tools to identify potential security gaps in your system, such as outdated software versions or misconfigured settings.
The objective of vulnerability scanning is to identify and categorize these vulnerabilities, prioritize them based on their severity, and provide recommendations for remediation.
Vulnerability scanning can be done both internally and externally, and it’s an essential security measure to ensure the integrity and availability of your systems and data. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities proactively, you can reduce the likelihood of cyber-attacks and minimize the impact of security breaches.
Vulnerability Scan Reports
Vulnerability scanning reports provide a detailed analysis of potential security gaps in a system, prioritizing them based on severity, and offering recommendations for remediation.
The reports typically include a list of identified vulnerabilities, along with their impact and severity ratings, and suggestions for mitigating the identified risks.
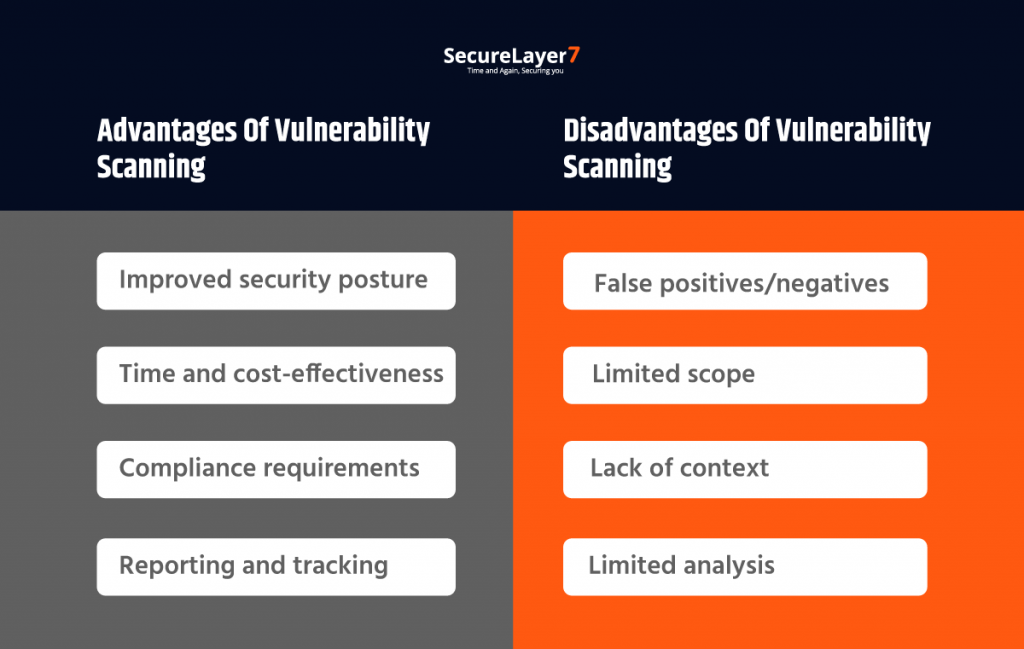
Advantages of Vulnerability Scanning
- Improved security posture: Vulnerability scanning helps organizations identify and address potential security gaps proactively, reducing the likelihood of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
- Time and cost-effectiveness: Automated vulnerability scanning is a quick and cost-effective way of identifying potential vulnerabilities in a system, compared to manual testing or remediation.
- Compliance requirements: Vulnerability scanning is often required by regulatory bodies, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, as a part of compliance requirements.
- Reporting and tracking: Vulnerability scanning reports provide an organized way of tracking and documenting security issues and their remediation efforts.
Disadvantages of Vulnerability Scanning
- False positives/negatives: Vulnerability scanning tools can sometimes generate false positive or false negative results, which can be time-consuming and expensive to address.
- Limited scope: Vulnerability scanning tools are only able to detect known vulnerabilities, and they cannot identify new or unknown threats that have not been previously identified.
- Lack of context: Vulnerability scanning reports provide a list of identified vulnerabilities, but they do not provide the context or understanding of the organization’s security posture.
- Limited analysis: Vulnerability scanning reports only provide a surface-level analysis of a system’s security posture and may not account for complex attack scenarios or exploits.
Overall, vulnerability scanning is an essential component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, but it should ideally be used in combination with other measures, such as penetration testing and security awareness training, to create a robust security posture.
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing, also known as “pentesting,” is a cybersecurity testing methodology that involves evaluating the security of a computer system or network by simulating an attack from an adversary.
The goal of a penetration test is to identify potential vulnerabilities in a system that could be exploited by malicious elements to gain unauthorized access, compromise data, or cause damage to the system.
The test typically involves a team of trained professionals who use a combination of automated tools and manual techniques to simulate various attack scenarios, such as exploiting software vulnerabilities, phishing, social engineering, or physical breaches.
The results of a penetration test can be used to improve the security posture of an organization, identify areas for improvement, and ensure compliance with security standards and regulations.
Reporting in Pentests
Penetration testing reports are typically more detailed and comprehensive than vulnerability scanning reports, providing a thorough analysis of the system’s security posture, including the identification of unknown and emerging threats.
They often include a prioritized list of vulnerabilities and recommended remediation actions, as well as detailed technical information for system administrators and developers.
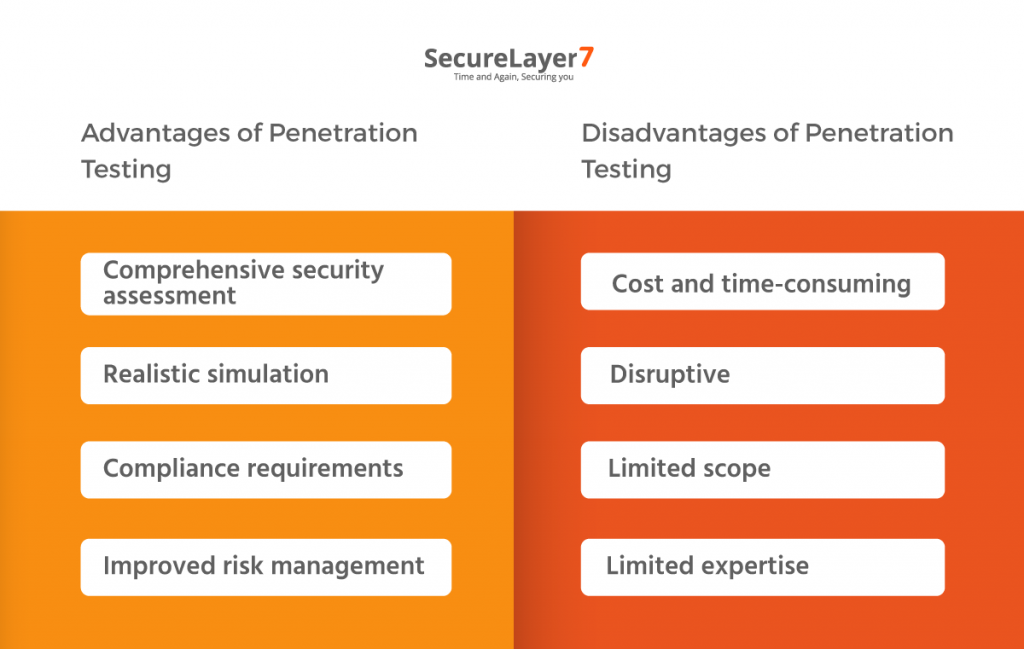
Advantages of Penetration Testing
- Comprehensive security assessment: Penetration testing provides a comprehensive assessment of a system’s security posture, identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses that may not be detected by vulnerability scanning or other measures.
- Realistic simulation: Penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios, providing a more realistic assessment of the system’s security posture and helping to identify potential attack vectors and how they can be mitigated.
- Compliance requirements: Penetration testing is often required by regulatory bodies, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, as a part of compliance requirements.
- Improved risk management: Penetration testing helps organizations prioritize and address security risks proactively, reducing the likelihood of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Disadvantages of Penetration Testing
- Cost and time-consuming: Penetration testing can be expensive and time-consuming, especially if it involves manual testing or custom-built exploits.
- Disruptive: Penetration testing can be disruptive to normal business operations, as it involves simulating attacks on the system.
- Limited scope: Penetration testing has a limited scope and may not uncover all security vulnerabilities or risks.
- Limited expertise: Penetration testing requires highly skilled professionals with specialized knowledge of security testing methodologies and tools.
Overall, penetration testing is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, providing a more realistic assessment of a system’s security posture and identifying potential vulnerabilities and risks that may be missed by other measures.
However, it should be used in combination with other security measures and should be conducted by reputable and experienced professionals to ensure its effectiveness.
Which One Best Suits Your Needs?

Choosing between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning can be a difficult decision for organizations.
The selection process should begin with understanding the specific goals and needs of the organization, the level of risk tolerance, and the available resources.
Vulnerability scanning is typically a more automated and cost-effective method of identifying potential vulnerabilities in a system, while penetration testing provides a more realistic assessment of a system’s security posture and identifies potential attack vectors.
It’s important to note that both methods are essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and should be used in combination with other measures, such as security awareness training and regular software updates.
When deciding between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, it’s essential to consider the scope of the assessment.
Vulnerability scanning is suitable for detecting known vulnerabilities in a system, while penetration testing is more appropriate for identifying unknown and emerging threats.
If an organization is seeking to comply with regulatory requirements, vulnerability scanning may be a more practical and cost-effective solution. On the other hand, if an organization has a low tolerance for risk and is seeking a more comprehensive security assessment, penetration testing may be the best approach.
Ultimately, the decision to choose between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning depends on the specific goals, needs, and resources of the organization.
Both methods are critical for maintaining a strong security posture, and they should be used in combination to provide a comprehensive assessment of a system’s security.
Organizations should consider working with experienced cybersecurity professionals to help them navigate the selection process and develop a customized security strategy that aligns with their unique needs and goals.
Get Comprehensive Pentests with SecureLayer7
Is your organization’s security posture vulnerable to cyber-attacks and data breaches? Do you need a comprehensive assessment of your system’s security to identify and mitigate potential risks?
Look no further than SecureLayer7’s penetration testing services.
Our team of experienced cybersecurity professionals uses the latest testing methodologies and tools to simulate real-world attack scenarios and identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your system’s security posture.
Our comprehensive testing services include network penetration testing, web application penetration testing, mobile application penetration testing, and social engineering testing.
Contact SecureLayer7 today to learn more about our penetration testing services and take the first step in securing your organization’s sensitive data and assets.


