
What is Data Lake? Understanding Data Lake Building Security
July 29, 2021
Dark Web Monitoring – Use Cases, Tools & Techniques
August 26, 2021
What is two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an essential security measure that enhances access security by demanding two distinct methods to verify one’s identity. It serves as an additional layer of protection beyond a user’s password when logging into an account.
The second factor of authentication can take the form of a code delivered through text messages or generated by authenticator applications. Alternatively, it can involve biometric features like fingerprint or face recognition.
Two-factor authentication is a specific type of multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to authenticate themselves through more than two different methods.
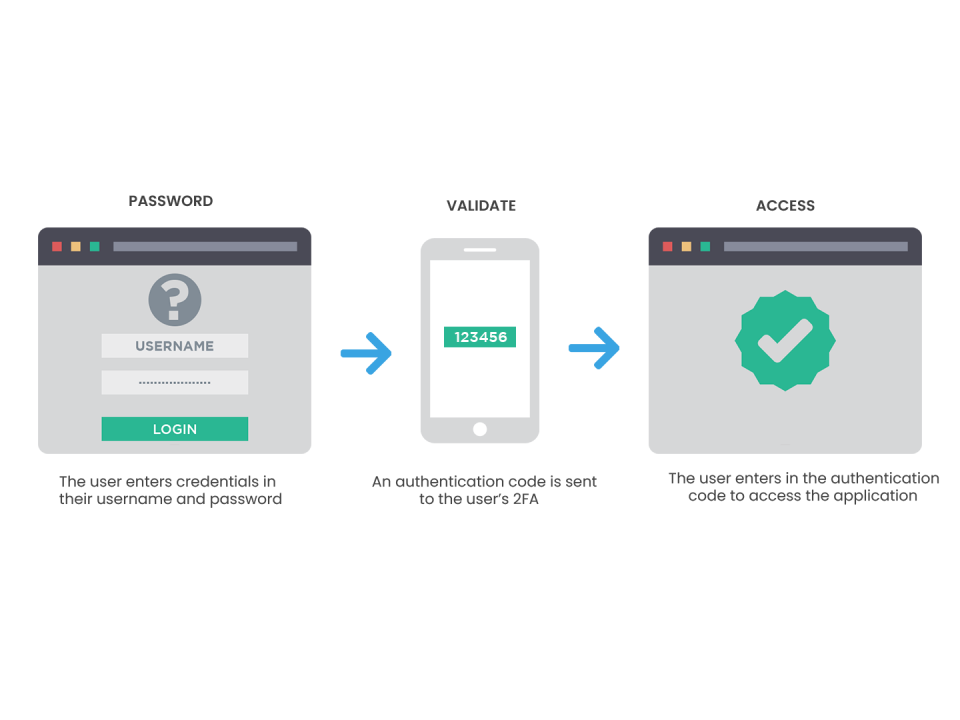
It is a subset of multi-factor authentication. In the case of multi-factor authentication, the user is required to identify himself/herself in more than two different ways.
Need for two-factor authentication
Let us have a look at some factors that imply the significance of two-factor authentication.
- Enhanced Security: Two-factor authentication significantly improves security by adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Even if a user’s password is compromised, an attacker would still need the second factor to gain access, making it much more difficult for them to breach the account.
- Mitigation of Password-Based Attacks: Password-based attacks, such as phishing, brute-force attacks, and credential stuffing, can be thwarted by implementing two-factor authentication. Even if an attacker obtains a user’s password through these methods, they would still require the second factor, making it nearly impossible to gain unauthorized access.
- Protection Against Stolen Credentials: Many users reuse passwords across multiple accounts, making them vulnerable to credential theft. If a user’s credentials from one service are compromised, the attacker may attempt to use the same login information on other platforms. Two-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access even if the login credentials are stolen.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries and regulatory bodies require organizations to implement two-factor authentication to protect sensitive information. These standards aim to safeguard user data, financial transactions, healthcare records, and other confidential data from unauthorized access.
- Mobile Device Dependency: With the widespread use of smartphones, two-factor authentication has become more accessible and convenient. Users can receive verification codes or approve login requests directly on their mobile devices, eliminating the need for additional hardware tokens and simplifying the authentication process.
- User Awareness and Trust: Implementing two-factor authentication demonstrates a commitment to security and can instill confidence in users. When users know their accounts are protected with an additional layer of security, they are more likely to trust the platform and feel more secure in their interactions.
- Business Protection: Two-factor authentication is beneficial not only for individual users but also for businesses. By implementing 2FA, organizations can protect their systems, databases, and sensitive information, reducing the risk of data breaches and potential financial losses.
Bypassing two-factor authentication
Bypassing 2FA using conventional session management
This method is about bypassing the two-factor authentication mechanism using password reset functions. In almost all web applications, the password reset function automatically logs the user into the application after the reset procedure is completed.
Bypassing 2FA Via the OAuth mechanism
As it is observed, in this process flow, there is no intervention of 2FA. An attacker can potentially abuse this mechanism and utilize an OAuth integration to log into the web application rather than using the username and password to do so.
Note:
For this bypass to work the attacker must have access to the OAuth integration account to log in on behalf of the user
Site.com requests Facebook for OAuth token= > Facebook verifies user account= > Facebook send callback code => Site.com logs a user in
Bypassing 2FA using blank code or null code
The application doesn’t check for null or empty code in the 2FA authentication process. Sometimes the 2FA can be bypassed by sending a blank code or null code.
{OTP:’123456′} => {OTP:”}
{OTP:’123456′} => {OTP:’null’}
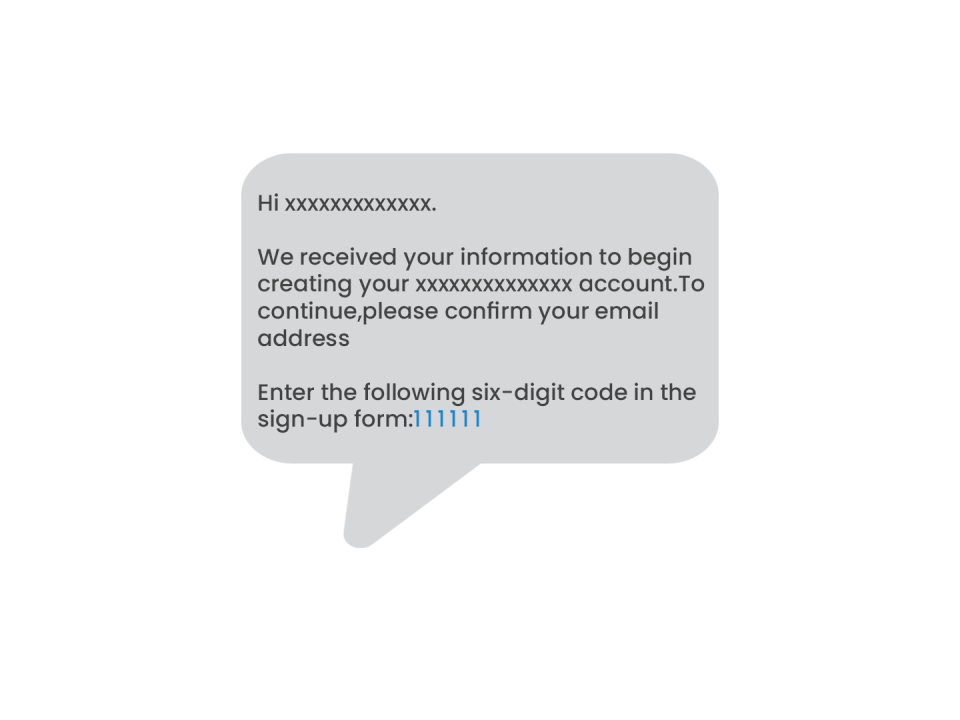
Bypassing 2FA using Guessable Values
Sometimes developers would set two-factor authentication codes with defaults values like 111111, 000000, 123456, etc.
1. Bypassing 2FA using Boolean values
This method is about bypassing the 2FA by changing the Boolean values.
First Scenario: An attacker can pass the value as “true” in the OTP parameter. If the application checks for boolean conditions then it can be bypassed.
{OTP:’23243′} => {OTP:’true’}
Second Scenario: An attacker can pass the value as “false” in parameters like OTP_Enabled or 2FA_enabled.
{mfa:’true’} => {mfa:’false’}
2. Bypassing 2FA using by removing OTP parameters
Sometimes 2FA is bypassed by completely removing the parameter and its values.
{email:’[email protected]’, password:’******”, otp:’323232′} =>
{email:’[email protected]’, password:’******”}
3. Bypassing 2FA using the Brute Force method
Usually, the length of the 2fa code is 4 to 6 characters which is often a number, and that makes to a possibility 151,800 which in a real-world scenario is easily brute force-able using a normal computer.
Advanced Brute Force Method: X-Forwarded-For: IP Header can be used to bypass Rate Limit Protection by spoofing the IP address.
X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1
4. Bypassing 2FA using Race Conditions
An attacker can utilize previously used or unused values of tokens to verify the device. However, this technique requires the attacker to have access to the previously generated values, which can be done via reversing the algorithm of the code generation app or intercepting a previously known code.
5. Bypassing 2FA using Response Manipulation
This method is about bypassing the 2FA by modifying the response.
First Scenario: Check if the response has any negative values when entering the wrong code.
Then change the value to a positive one.
{success:’false’} => {success:’true’}
{valid:’false’} => {valid:’true’}
{success:’0′} => {success:’1′}
Second Scenario: Try to find the valid status code when entering the correct code. Now give any wrong OTP code and check the response code if it’s something like 3xx, 4xx then try to change it to 200 OK and see if it bypasses restrictions.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request => HTTP/1.1 200 OK
6. Bypassing 2FA using Activation/Confirmation link
An attacker is able to log in with an activation/confirmation link due to a lack of token expiring. It can be reused many times to bypass the two-factor authentication.
7. Bypassing 2FA using Leaked Token
An application sometimes leaks a token in the response body or in the referrer header. So it’s important to look for that information while performing a 2FA bypass.
8. Bypassing 2FA using Direct Access
Note down all endpoints of the application and try to access those endpoints directly before the 2FA authentication process.
https://test.test.com/2FA/auth => https://test.test.com/dashboard
While two-factor authentication is an essential security measure, it is crucial to stay informed about the bypass techniques employed by attackers.
By understanding these methods and implementing appropriate security measures, individuals and organizations can enhance their defenses and safeguard their accounts and sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Vigilance, user education, and the adoption of robust security practices are vital in maintaining a strong security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Summing Up
In conclusion, as two-factor authentication became a widely adopted security measure, hackers developed sophisticated techniques to bypass it.
Man-in-the-Middle attacks intercept communication to capture authentication codes. As technology evolves, it is crucial for individuals and organizations to stay vigilant, adopt additional security measures, and prioritize continuous advancements in authentication methods to stay one step ahead of potential attackers.
To keep reading such blogs on the trends and happenings in the realms of cybersecurity, follow SecureLayer7 .
Reference links:
1.https://shahmeeramir.com/4-methods-to-bypass-two-factor-authentication-2b0075d9eb5f
2. https://kishanchoudhary.com/2fa/bypass.html
3. https://gauravnarwani.com/two-factor-authentication-bypass/
4. https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/2fa-bypass


