
Pentesting For GCP security – Fortifying Google Cloud
March 13, 2023
Network Security Best Practices: A 15-Point Checklist
March 14, 2023
In today’s interconnected world, networks are an essential component of every organization’s infrastructure.
However, this increased connectivity also means that networks are vulnerable to cyber attacks, making securing them against unauthorized access critical.
One way to ensure network security is through network penetration testing, which involves simulating a cyber attack to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in a network’s security defenses.
Network security testing is an essential aspect of cybersecurity and is often required to meet compliance standards and regulatory requirements.
This process involves a comprehensive assessment of a network’s security posture, including its hardware, software, and network configurations, to identify and address potential security weaknesses.
This blog will provide a complete guide to network pentesting, covering its importance, types of tests, methodology, tools, and best practices.
We will also discuss how to plan and execute a successful network penetration testing project, including interpreting test results and addressing any identified vulnerabilities.
By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of network penetration testing and be equipped to implement it effectively to secure your organization’s networks against cyber threats.
What is Network Penetration Testing?
Network Penetration Testing is a cybersecurity process in which a security professional attempts to simulate an attacker’s activities to identify vulnerabilities and potential entry points in a network’s security defenses.
Networks are highly intricate, consisting of a blend of WAN, LAN, and wireless networks, a vast number of endpoints that encompass servers, workstations, mobile devices, internet of things (IoT) devices, and security technologies such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
Any of these components could present a potential vulnerability, making it possible for attackers to exploit and gain unauthorized access to the network.
The goal of network penetration testing is to assess the network’s security posture and identify any security weaknesses before a real cyber attack occurs.
Importance of network pen-testing
Network penetration testing is crucial for organizations to ensure the security of their networks and protect against cyber attacks. The importance of network pen-testing can be summarized as follows:
- Identify vulnerabilities: Network penetration testing helps to identify vulnerabilities and security weaknesses in the network before an attacker exploits them. By identifying these vulnerabilities, organizations can address them before they become a security risk.
- Improve security posture: Pen-testing provides valuable insights into the security posture of an organization’s network, allowing them to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about security investments.
- Meet regulatory requirements: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are required to comply with regulatory standards such as HIPAA and PCI DSS. Network pen testing is often required to meet these standards.
- Reduce financial loss: A successful cyber attack can result in significant financial loss for organizations. By identifying vulnerabilities and improving security defenses, network pen-testing can help to reduce the financial impact of a cyber-attack.
- Protect company reputation: A cyber attack can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and business. Network pen-testing can help to protect the organization’s reputation by identifying and addressing security weaknesses before they are exploited.
Overall, network penetration testing is a critical aspect of cybersecurity and is essential for organizations to protect against cyber threats, meet regulatory requirements, and maintain the trust of their customers.
Most common network security threats
There are many network security threats that organizations face in today’s digital landscape. Here are some of the most common threats:
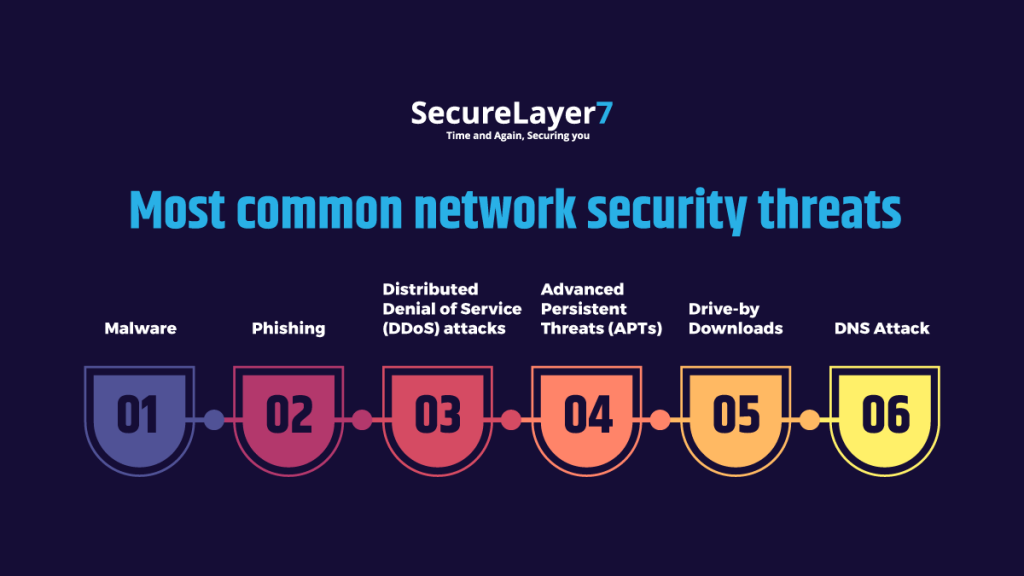
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to damage or disrupt computer systems. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, and trojan horses. Malware can be spread through email attachments, malicious websites, or software downloads.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which attackers attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials or financial information. Phishing attacks can be conducted through email, social media, or messaging platforms.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
A DDoS attack is an attempt to make a website or network unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic. This can be done through a botnet, a network of computers that have been infected with malware and can be controlled remotely.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are a type of sophisticated cyber attack in which attackers gain unauthorized access to a network and remain undetected for an extended period, often months or even years.
The attackers use a combination of social engineering, malware, and other tactics to gain access to the network, and once inside, they continue to target sensitive information or systems.
Unlike other types of cyber attacks, APTs are targeted and often customized to a specific organization or industry.
The attackers use information obtained from reconnaissance activities to develop a tailored attack strategy that is difficult to detect and mitigate.
Drive-by Downloads
Drive-by downloads are a type of malicious software download that occurs when a user visits a website or clicks on a link, often without realizing it.
The malicious software is automatically downloaded and installed on the user’s device, without any user interaction or consent.
Drive-by downloads are often used to distribute malware such as viruses, Trojans, and ransomware.
Drive-by downloads are a type of malicious software download that occurs when a user visits a website or clicks on a link, often without realizing it.
The malicious software is automatically downloaded and installed on the user’s device, without any user interaction or consent.
Drive-by downloads are often used to distribute malware such as viruses, Trojans, and ransomware.
DNS Attack
A DNS attack is a type of cyber attack that targets the Domain Name System (DNS), which is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. DNS attacks can have serious consequences, as they can disrupt an organization’s ability to access critical resources or compromise sensitive data.
There are several types of DNS attacks, including:
- DNS Spoofing: In this type of attack, attackers manipulate the DNS cache to redirect users to a malicious website instead of the intended website.
- DNS Cache Poisoning: Attackers inject false DNS information into the cache of a DNS server to redirect users to a malicious website.
- DNS Amplification: In this type of attack, attackers use a DNS server to amplify the size of a DDoS attack, making it more difficult to mitigate.
- DNS Tunneling: This involves encapsulating data in DNS queries and responses, allowing attackers to bypass firewalls and other security measures.
To prevent DNS attacks, organizations can implement security measures such as using DNSSEC to secure DNS transactions, using firewalls to restrict DNS traffic, and monitoring DNS traffic for suspicious activity.
Overall, these network security threats can cause significant damage to organizations and their networks.
It’s essential to have proper security measures in place, including regular network penetration testing, to identify and mitigate these threats.
Internal vs external penetration testing – An Overview
Internal and external penetration testing are two different approaches to assessing an organization’s network security.

Both internal and external penetration testing are important for a comprehensive security assessment.
Internal testing can identify vulnerabilities that external testing may miss, while external testing can identify vulnerabilities that internal testing may not be able to access.
By combining both approaches, organizations can gain a more complete understanding of their network security posture and better prepare for real-world cyber attacks.
The Complete process for network pen testing
Here’s a breakdown of the process for network penetration testing into individual points:
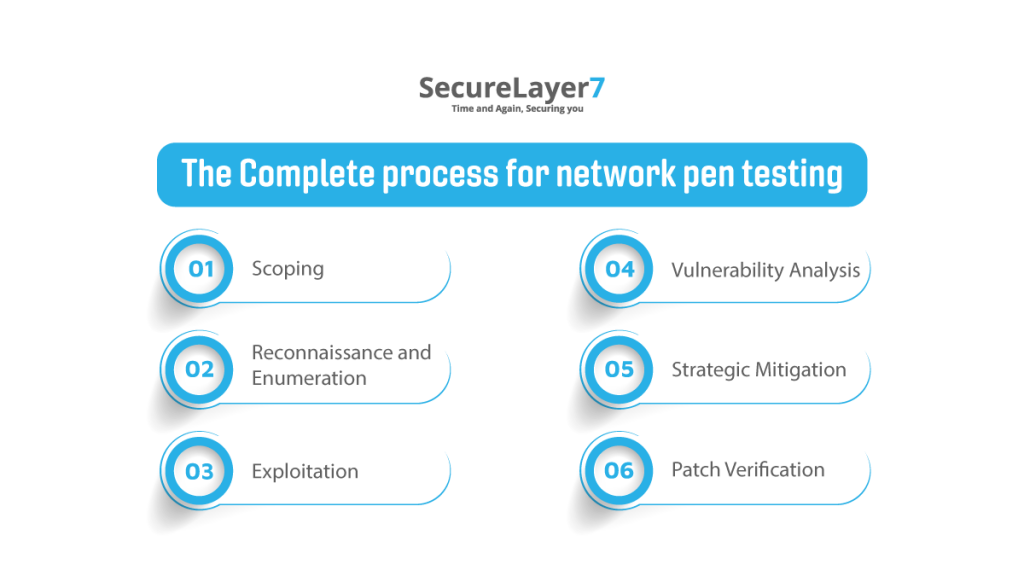
Step 1 – Scoping:
- Define the scope of the test, including the systems and devices to be tested and the testing methods to be used.
- Obtain permission from the organization that owns the network to conduct the test.
- Identify the objectives of the test and define the rules of engagement.
- Define the timeline, resources, and budget for the test.
Step 2 – Reconnaissance and Enumeration:
- Collect information about the target network, such as IP addresses, network topology, operating systems, and services running on each host.
- Use tools such as port scanners, network mappers, and vulnerability scanners to gather information about the target network.
- Identify potential entry points and vulnerabilities in the network.
Step 3 – Exploitation:
- Use automated tools and manual techniques to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network.
- Attempt to exploit the vulnerabilities to gain access to the target network.
- Use tools such as Metasploit, Nmap, and Burp Suite to launch attacks on the network.
Step 4 – Vulnerability Analysis:
- Analyze the vulnerabilities that were identified to determine their severity and potential impact on the network.
- Prioritize the vulnerabilities based on their risk and exploitability.
- Provide recommendations for remediation and mitigating the vulnerabilities that were identified.
Step 5 – Strategic Mitigation:
- Develop a strategic plan for mitigating the vulnerabilities that were identified.
- Define the steps that the organization can take to improve the security of the network.
- Provide guidance on best practices for network security.
Step 6 – Patch Verification:
- Verify that the patches and security measures implemented by the organization have successfully remediated the vulnerabilities.
- Test the network to ensure that the vulnerabilities have been fully mitigated.
- Provide a report detailing the results of the testing and any remaining security concerns.
Overall, network penetration testing is a complex and specialized process that requires significant expertise and experience. It is recommended that the testing be conducted by trained and certified professionals.
Fortify your network with comprehensive penetration testing from SecureLayer7
Is your organization’s network secure against cyber attacks? With the increasing number of cyber threats today, it’s crucial to ensure your network is protected against potential vulnerabilities.
That’s where SecureLayer7 comes in. Our comprehensive penetration testing services help you identify weaknesses in your network, applications, and devices, so you can take the necessary steps to fortify your network against cyber threats.
Our team of experienced professionals uses advanced tools and techniques to conduct rigorous testing that simulates real-world attacks.
We provide you with a detailed report on the vulnerabilities we find, along with recommendations for remediation and mitigation.
With our comprehensive penetration testing, you can rest assured that your network is secure against cyber attacks. Contact SecureLayer7 and see how you can protect your organization’s sensitive data and assets.


