
What is WAF (Web Application Firewall), And How Do You Bypass It?
November 10, 2022
The Definitive Guide To Web Service Security Penetration Testing
November 25, 2022
What is WAF (Web Application Firewall), And How Do You Bypass It?
November 10, 2022
The Definitive Guide To Web Service Security Penetration Testing
November 25, 2022A data lake is a simple, scalable, and cost-efficient storage option that allows companies to securely store a considerable amount of their sensitive data.
Although, with newer attack vectors emerging every day, businesses need to employ the best practices in data security to safeguard themselves from potential vulnerabilities and breaches.
With a growing list of companies moving their databases to cloud storage to avail the benefits of data lakes, it has never been more important to discuss why you should enforce the best practices in data lake security.
This article explores data lake security and the practices companies can leverage to guard their invaluable data.
What is a data lake?
Data lakes are centralized repositories where you can store structured and unstructured data in its original format. This data can subsequently be subject to robust analytics to drive better organizational decision-making.
They also enable owners to share a portion rather than the entirety of the company data to stakeholders contingent upon the individual user’s duties, necessities, and responsibilities.
The business’s data security and access policy protects the organization from leaks, breaches, and employee misconduct by dictating the data handling terms between all parties involved.
The need for data lake security
An advantage of data lakes is their ability to allow businesses to store a potentially unlimited amount of data centrally. This storage option enables firms to perform analytics, conduct investigations, identify threats, and maintain compliance.
Companies can also perform crawling, cataloging, and indexing on the stored operational and application data to streamline business operations.
Although with the emergence of big data as a significant driver of business success, bad actors are constantly devising new methodologies to target and compromise data lake security. In such instances, businesses face hefty financial and reputational damages, which is precisely why beefing up your data lake security should be of the utmost importance.
Here are some fundamental techniques businesses should employ to secure their data lakes:
Authorization
Protecting valuable company information requires assigning specified data access and control to individuals contingent on their expertise and organizational designations.
It is an excellent practice to authorize those requiring high clearance to manage and edit the data lake while keeping other lower-level stakeholders with restricted view-only access.
Encryption
Data encryption is a cryptography method that improves data security by deliberately scrambling data and making it inaccessible without a decryption key. In most cases, the decryption capability is provided only to users with the appropriate clearance to access the data.
Encryption is an added security layer for data lakes that helps them stay secure from bad actors.
Authentication
Without proper user authentication, bad actors can use tactics such as social engineering to acquire employee credentials and quickly gain access to business data while disguising themselves as authorized stakeholders.
Authentication is an effective mechanism that helps prevent this by ensuring that the system verifies a user’s true identity before granting access to the data.
Some commonly used authentication methodologies are usernames, passwords, multi-factor identification, and multi-device authentication.
But is there more you can do to ensure data lake security?
Authorization, encryption, and authentication are fundamental defense mechanisms to uphold when dealing with large amounts of confidential data.
However, it is worth knowing that modern-day cyber criminals constantly develop numerous hacks and workarounds that can defeat these security measures.
For businesses to decrease their attack surface even further, creating a data lake security plan that best suits your business requirements is paramount.
Creating a data lake security plan
An effective data lake security plan can help businesses protect their data on a higher level by enforcing the best practices in data access control, protection, lake usage audits, leak prevention, and security policy governance and compliance.
Let us dive into these aspects and understand what it means to your data lake security.

Data access control
Data is segregated and stored within the lake as objects, each containing a unique collection of files. Users can freely view and modify these files when granted access to their native object.
This unfettered freedom to modify files is problematic because even though stakeholders can detect any data modification, the exact nature of the changes can sometimes take time to authenticate.
Adding more complexity to the problem is that it becomes increasingly challenging for businesses to pinpoint the stakeholder behind the changes when numerous members have access.
A robust data security plan must ensure that the proper identity and access management (IAM) systems are in place, providing remote control over which users have the appropriate clearance to modify the data.
The goal behind proper data access control should be to give the managers and data stewards the right tools and systems to deploy granular permissions to individual users based on their access level requirements.
Data protection
Data encryption is a gold standard for cyber security, which provides varying levels of security based on the type of encryption you choose that best suits your requirements.
However, a common problem businesses encounter with encryption is that it changes the file’s data type and makes it challenging for applications to process the data.
While decryption keys are highly effective, they can be misplaced or stolen if not stored securely, which could result in a catastrophic data breach.
A more effective approach to data protection would be using a combination of cloud encryption and tokenization. While tokenization will protect the data while maintaining the original data types, encryption will allow you to block malicious actors attempting to gain unauthorized access.
Data lake usage audit
We have observed that a data owner’s biggest concern is the criterion data stewards consider when granting users access to sensitive data.
Another concern facing data owners is the quantity of sensitive data added to the lake and what applications should have access to it. Data owners also need to track how much data is accessible to stakeholders.
These concerns mainly arise because when internal or external data leaks occur, it is hard to pinpoint the origin and extent of a breach when a myriad of users have access to the data lake.
This problem is why it is paramount for data owners to maintain comprehensive communications with stewards and conduct periodical data lake usage audits to ensure that data security is invariably upheld.
These audits also ensure that data oversight and governance are up to par before providing stakeholders access to the data lake.
Data leak prevention
Rich data not only opens up countless business opportunities but can also be highly detrimental when it leaks into the wrong hands. Data owners must understand that most leaks originate from employee misconduct or substandard security practices.
While in some instances, the leak may occur due to employee negligence, like losing their credentials to more outrageous situations where employees misuse their access privileges for malicious financial gain.
Either way, it is essential to restrict the data exposure to every user at a more granular level. Even the slightest mistakes in granting permissions can cause severe business harm both financially and reputationally.
The best way to ensure these occurrences do not occur is to deploy effective policies combined with periodical data audits based on stakeholder usage.
These audits secure the data lake by swiftly identifying and notifying the relevant authorities of any suspicious activity or blatant company data misuse by internal or external actors.
Data governance and compliance
The laws around data governance and compliance are subject to constant change and differ from region to region.
As these regulations change and adapt to emerging industry conditions, the data governance team must ensure that stakeholders adhere to current policies and stay updated on any relevant policy changes.
This practice, centered on continual training and awareness exercises, empowers businesses to safely handle the sensitive data stored within the data lakes and achieve higher organizational compliance.
Another point to remember is to always focus on employing the right technologies to access, handle and store your sensitive data that keeps you adherent to all policy present and emerging policy norms.
Data lake security best practices
To help businesses achieve the highest level of data lake security, we have compiled a list of best security practices to follow. They are:
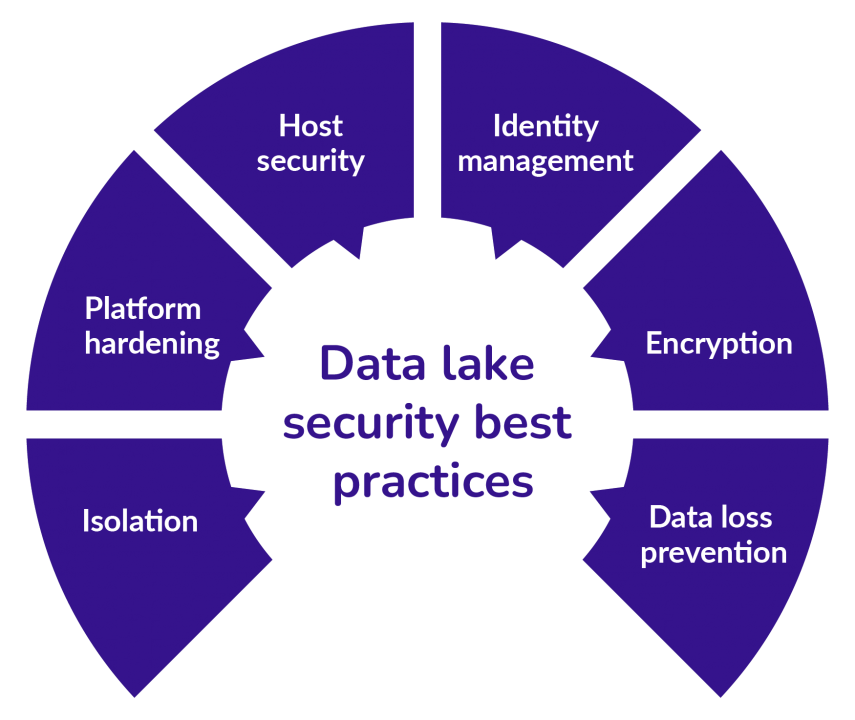
Isolation
When providing data access to a large group of people, it is crucial to understand each user’s expertise and role definitions and to whom data access is an absolute necessity. Isolation helps effectively handle such situations by enabling data owners to streamline and restrict data access down to a need-to-know basis.
Additionally, it is necessary to place restrictions on the integrated cloud platforms that access and draw information from the data lakes.
These practices should be the golden standard all businesses must follow when building the foundation of their cloud security to avoid expensive and damaging data breaches.
Platform hardening
Potential attack vectors arise daily through cloud services connected to your data lake.
To protect yourself from such risks, it is a good practice to reduce your attack surface by conducting platform hardening, which uses a combination of model configurations, techniques, tools, and approaches to reduce vulnerabilities that materialize from connected applications and cloud services.
Host security
Host security provides businesses with an appropriate framework to identify, monitor, and log any host-based attacks on a targeted data lake.
These systems often act as the final line of defense that maintains data integrity by protecting it from unwarranted intrusions.
Identity management
Practicing good identity management can be a crucial preventative measure against unauthorized intrusions.
A robust cloud-integrated identity management system allows businesses to monitor and maintain the correct access levels of employees and external vendors in real-time.
Encryption
Encryption must always be a standard practice when creating and deploying data lakes. Your encryption should protect all types of data present in the centralized repository.
When encryption is applied, it is vital to watch out for expired, expanding, or new constraints placed on existing certificates that can pose a significant security risk.
Practicing periodical certificate rotation can help reduce encryption vulnerabilities and maintain optimal data lake security.
Data loss prevention
The value of data is undeniable, and businesses must devise how it is stored and managed to avoid such circumstances.
Employ all technologies, storage mechanisms, tools, and practices necessary, and most importantly, conduct periodic checks and evaluations of all storage devices to prevent data loss.
To Conclude
The best practices in isolation, platform hardening, host security, identity management, encryption, and data loss prevention are essential to safeguard your data lakes.
Isolation and identity management are additional tools that go hand-in-hand toward reducing your attack surface from attacks originating internally. It is vital that you also address all attack vectors that arise as a result of integrating multiple cloud services into your data lake.
Suppose your current data lake security measures need to be revised, consider consulting with an external service provider with the experience and expertise to provide the necessary assistance to secure your data.
SecureLayer7 provides penetration tests on all leading platforms businesses use to build and maintain data lakes, such as AWS, Microsoft AZURE, and Kubernetes, providing comprehensive protection for your data.
We are well-known amongst businesses and SME organizations that use our penetration testing application to perform and act on continuous pentests.
We help you uncover twice the number of critical vulnerabilities in your AWS infrastructure and improve the security and compliance of all its integrated applications. Our cloud security audits help address any security issues in your configurations while ensuring they comply with regulations such as SOC3, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and others.
Strengthen your cloud data lake security by leveraging our services to test the cloud console and hosted internal and external applications to prevent layer 7 DDoS attacks.
Our PaaS services include application testing, mobile app penetration testing, thick client penetration testing, source code analysis, smart contract audit, and cloud penetration testing. SecureLayer7 can also help you scan and review all hardware devices, firewall accounts, malfunctions, rulesets, vulnerabilities, licenses, and services. We will guide you through every step of the way on all the best practices available to reduce the attack surface of your data lake. Contact us now to find out more.