
Understanding the Cost and Impact of Data Breaches
October 19, 2023
CyberFlicks: Top 10 Hacker Movies
October 30, 2023
In today’s increasingly digital world, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated, particularly in the healthcare sector.
With the rapid adoption of electronic systems and the digitization of patient records, ensuring the protection of sensitive information and assets has become a paramount concern.
Cybersecurity in healthcare involves the implementation of measures and practices to safeguard electronic information from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure. Its overarching objective is to uphold the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, commonly referred to as the “CIA triad.”
Let us delve into the world of cybersecurity in healthcare, exploring its significance, challenges, and the strategies employed to safeguard this vital information.
What is Cybersecurity in Healthcare?
Cybersecurity in healthcare encompasses a set of practices, policies, and technologies designed to protect electronic information and assets within the healthcare industry.
In an era where patient records and medical data are increasingly stored and accessed digitally, it is crucial to safeguard these sensitive resources from potential threats and breaches.
At its core, cybersecurity in healthcare focuses on maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, following the principles of the “CIA triad.”
Confidentiality ensures that patient data remains private and accessible only to authorized individuals. Integrity ensures that data is accurate, complete, and unaltered. Availability ensures that data is accessible and usable when needed.
Challenges Faced in Healthcare Cybersecurity
We have listed some of the pivotal challenges that persist in healthcare cybersecurity.
- Patient privacy protection
- Patient privacy informational resources
- Email attacks (phishing attacks)
- Vulnerabilities of Legacy Systems in Healthcare

Patient privacy protection
Ensuring the privacy of patient information is one of the foremost challenges in healthcare cybersecurity.
The sensitive nature of medical data, including personal and health-related information, makes it an attractive target for cybercriminals.
Healthcare organizations must employ robust measures to protect patient privacy and prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of this data.
Patient privacy informational resources
To address the challenge of patient privacy protection, healthcare organizations can utilize various informational resources.
These resources provide guidelines, best practices, and regulatory requirements for safeguarding patient information.
They help healthcare professionals stay informed and updated on the latest privacy standards, ensuring compliance and the protection of patient privacy rights.
Email attacks (phishing attacks)
Phishing attacks pose a significant threat to healthcare organizations. Cybercriminals often use deceptive emails to trick employees into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware.
These attacks can lead to data breaches, ransomware infections, and compromise the security of patient information.
Vulnerabilities of legacy systems in Healthcare
Legacy systems, despite their outdated nature, are still prevalent in many healthcare organizations.
These systems often lack necessary security updates and are more susceptible to cyber threats. However, transitioning to newer systems can be challenging due to factors such as budget constraints, interoperability issues, and the need for extensive staff training.
Despite the Benefits Digitization Provides, Many Healthcare Systems Keep Outdated Legacy Systems for the Following Reasons:
- Cost considerations
- Complexity of Migration
- Interoperability challenges
- Retraining staff
- Potential disruptions to healthcare services
- Legacy system customization
- Regulatory compliance concerns

Challenges of IT in Healthcare
The integration of information technology (IT) in healthcare brings about its own set of challenges. Healthcare organizations need to strike a balance between embracing technological advancements and ensuring the security and privacy of patient data.
IT systems must be reliable, scalable, and resistant to cyber threats to support efficient healthcare operations and improve patient outcomes.
IT Opportunities in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations can leverage various resources that highlight the opportunities and benefits of IT in the industry.
These resources provide insights into the latest technological advancements, their potential applications in healthcare, and how they can address the challenges faced by healthcare IT professionals.
Security Breaches in Healthcare
Security breaches pose a significant risk to healthcare organizations, potentially compromising patient data, disrupting services, and damaging the reputation of the organization.
Understanding common types of security breaches can help healthcare professionals better prepare and implement preventive measures.
6 Common Types of Security Breaches in Healthcare
- Data breaches
- Ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
- Malware infections
- Social engineering attacks
- Physical theft or loss of devices

Security Strategies in Healthcare
To mitigate security breaches, healthcare organizations can access resources that provide strategies and best practices for enhancing cybersecurity.
These resources offer guidance on implementing robust security measures, incident response planning, staff training, and staying updated on the latest threats and countermeasures.
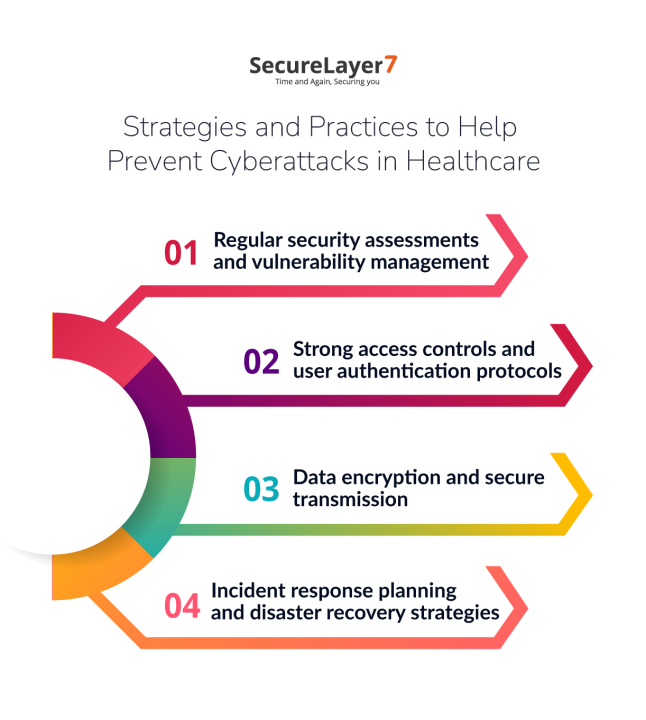
Strategies and Practices to Help Prevent Cyberattacks in Healthcare
Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity framework is crucial for preventing cyberattacks in healthcare. This includes measures such as:
- Regular security assessments and vulnerability management
- Strong access controls and user authentication protocols
- Data encryption and secure transmission
- Employee training and awareness programs
- Incident response planning and disaster recovery strategies
Cybersecurity in Healthcare Best Practices
In the digital age, cybersecurity is of paramount importance, especially in the healthcare sector where sensitive patient data is stored and transmitted.
Healthcare organizations must establish robust cybersecurity measures to protect patient privacy, maintain data integrity, and prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
This section will delve into best practices for cybersecurity in healthcare, focusing on risk assessments and security controls.
Risk Assessments
A comprehensive risk assessment forms the foundation of an effective cybersecurity strategy in healthcare. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, assessing the likelihood and impact of threats, and determining the appropriate safeguards. Conducting regular risk assessments allows healthcare organizations to proactively identify and address potential security gaps. Here are key steps involved in performing risk assessments:
- Identifying Assets: Begin by identifying all the valuable assets within the healthcare organization, including electronic health records (EHRs), medical devices, and network infrastructure.
- Threat Identification: Identify potential threats that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of these assets. Examples include malware, insider threats, physical theft, and social engineering attacks.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Assess the vulnerabilities within the healthcare organization’s systems and networks. This may involve conducting penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews to identify weaknesses that could be exploited.
- Risk Analysis: Evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of each identified threat. This analysis helps prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively to mitigate the most critical ones.
- Risk Mitigation: Develop and implement a risk mitigation plan that addresses the identified vulnerabilities. This plan should include technical controls, employee training, and incident response protocols.
By regularly conducting risk assessments, healthcare organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats, enhance their security posture, and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data.
Security Controls
Implementing robust security controls is crucial to safeguarding healthcare systems and data from unauthorized access or breaches.
These controls include a combination of technical, administrative, and physical measures. Let’s explore both basic and advanced security controls commonly employed in healthcare environments.
Basic Security Controls
Access Control: Implement strong access controls to limit system and data access to authorized personnel only. This can involve strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls (RBAC).
Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access. This includes utilizing strong encryption algorithms and secure key management practices.
Regular Patching and Updates: Keep software, operating systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches. Regular patching helps address known vulnerabilities and protect against exploits.
Employee Education and Awareness: Provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to all employees, emphasizing the importance of secure practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious websites, and maintaining strong passwords.
Advanced Security Controls
Network Segmentation: Segment the network into secure zones to limit the lateral movement of threats. This practice prevents the compromise of critical systems if one part of the network is breached.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS to monitor network traffic for suspicious activities, detect potential threats, and block or mitigate attacks in real-time.
Endpoint Protection: Utilize advanced endpoint protection solutions, including anti-malware, host intrusion prevention systems (HIPS), and behavior-based detection, to defend against advanced threats targeting individual devices.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan and disaster recovery strategy to ensure a swift and effective response to cybersecurity incidents. This includes backup and restoration procedures, as well as communication protocols.
By implementing these basic and advanced security controls, healthcare organizations can significantly strengthen their cybersecurity posture and minimize the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to patient information.
Cybersecurity in Healthcare: Summing Up
In summary, cybersecurity is a critical aspect of healthcare operations. Risk assessments provide a systematic approach to identifying vulnerabilities, assessing threats, and implementing appropriate safeguards.
By conducting regular risk assessments, healthcare organizations can proactively address potential security gaps and enhance their overall security posture.
Security controls, both basic and advanced, are essential for protecting healthcare systems and data. Basic controls such as access control, encryption, regular patching, and employee education, provide a foundation for cybersecurity best practices.
Advanced controls, including network segmentation, IDPS, endpoint protection, and incident response planning, further bolster security defenses.
By prioritizing cybersecurity and adhering to these best practices, healthcare organizations can safeguard patient data, maintain trust, and ensure the delivery of quality healthcare services in an increasingly digital landscape.


