
Why Is Gartner Talking About External Attack Surface Management (EASM)
February 9, 2022
Spring4Shell RCE a new Vulnerability in Spring Framework via Data Binding
April 2, 2022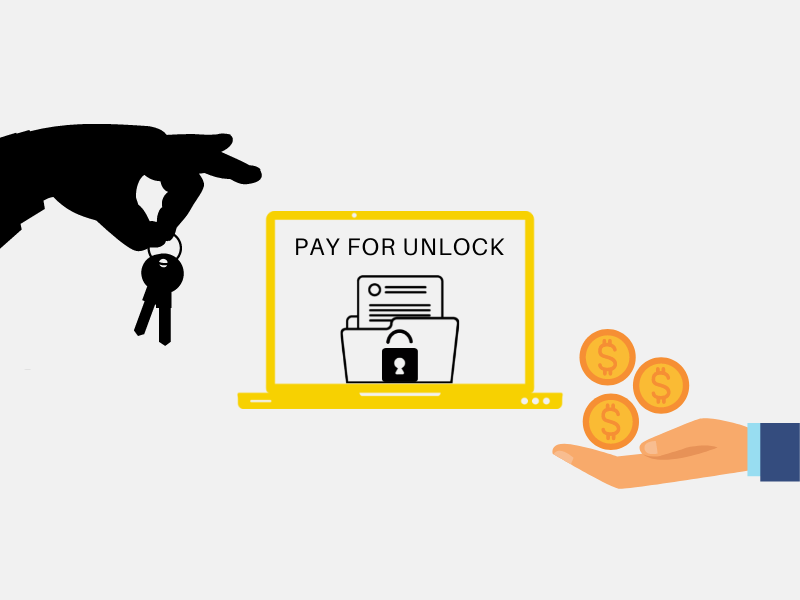
Hello there!
Today we will discuss something scary but interesting: The “Ransomware attack”. Occasionally we hear from people about their data being tied up, and it’s not accessible. This happens due to malware attacks.
Malware is malicious software that is usually attached to the email, embedded in links, hidden in ads at various sites that your employees might visit on the internet.
It is used to harm or exploit computers and networks so that the attackers can then steal the data.
What is a Ransomware attack?
There are several types of malware (Worm, Trojan, viruses ), and Ransomware is one of the most potent malware. Malware attacks block users data; users can’t access their data and receive a ransom notification. Ransomware restricts users’ access to files on computers or mobile devices.
it encrypts all data until the user pays the ransom.
A ransomware attack can happen to any user, but attackers mostly target organisations such as IT, technology and telecoms, Financial services, Education etc. An organisation considers the loss of data as they have valuable information regarding their product or modules, which is why, if an organisation’s data is compromised, they have to pay the ransom.
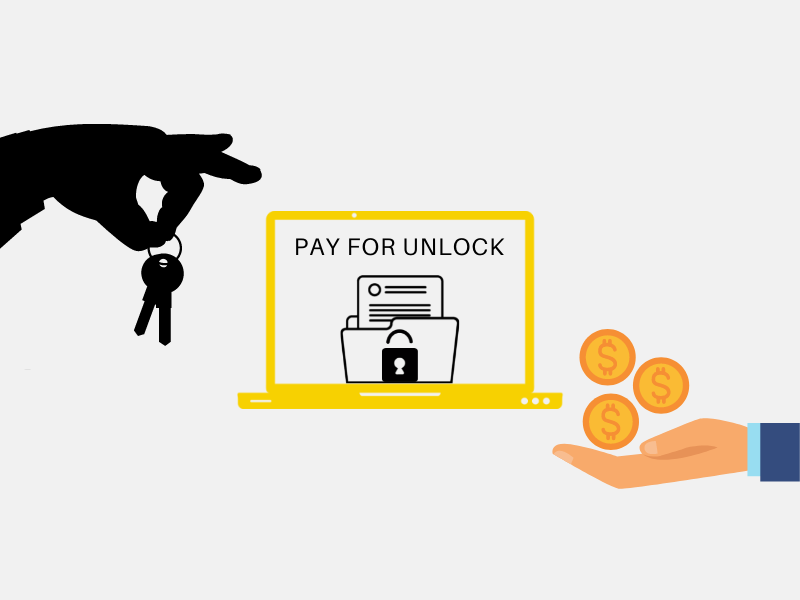
Process of Ransomware Attack
Nowadays we spend a lot of our time surfing through the internet, searching for valuable information, doing official work, mail checking etc.
Users receive random emails from organisations, cell phone companies, banks and friends regarding products or schemes. Some of these emails are phishing emails. A phishing mail consists of a link. When the user clicks on that link, a file (generally a zip file) is automatically downloaded into their system.
As soon as the user opens that zip file, the malicious payload is executed automatically in PowerShell, and files, data, and personal information are compromised. And then, a window will appear on our screen asking for ransom. Ransom can be money or cryptocurrency. Users will have the system, but they can’t access it. And even if the user can pay the ransom, there is no guarantee that the hacker will give them back their access.
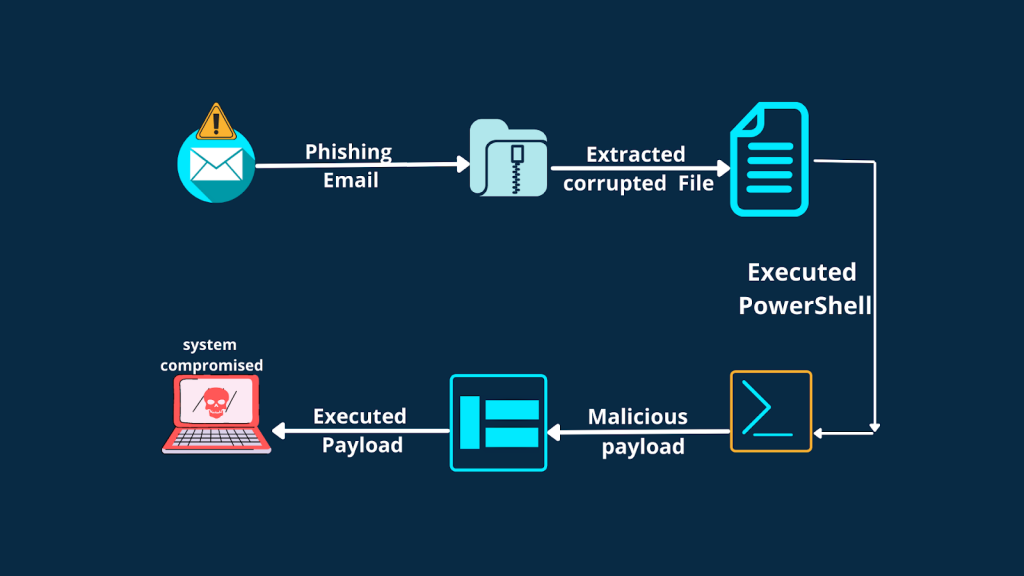
Ransomware Attacks On Companies/Organizations.
For the past few years, numerous companies and organisations have been targeted with ransom attacks. Some of those organisations had paid the ransom and still haven’t got back their data. The stolen data has been sold to organisations or has been leaked.
During the COVID pandemic, ransomware attacks have had a huge financial impact on the healthcare sector. Companies and Organizations have been attacked by ransomware.
- ACER – ACER is a computer manufacturing company was attacked by the REvil hacker group, and the ransom they got is $50 million aaprox. REvil hackers exploited a vulnerability in a Microsoft Exchange server to access Acer’s files and leaked images of sensitive financial documents.
- BRENNTAG – Brenntag, a chemical distribution company, was attacked by a notorious hacker group. The hacker group demanded $7.5 million in bitcoin, but they settled for $4.4 million dollars bitcoin.
CNA – CNA, a financial corporation company, was attacked by the Evil Corp hacker group. They encrypted almost fifteen thousand devices from CNA’s servers, and the CNA company almost paid $40 million ransom.
- QUANTA – Quanta, a Computer Manufacturing company and is one of Apple’s major business partners, was attacked by theREvil hacker group, and they demanded a $7.5 million ransom.
- CD Project – CD Project, a Polish video game development company, was hacked by the HelloKitty hackers group. They encrypted devices and got access to game projects source code in development.
Types of Ransomware Attacks
We know that there are several variants available of ransomware. New types of variants are being programmed for particular purposes as I am typing this.
Here we listed some common ransomware types.
- Locker ransomware – This type of ransomware blocks basic computer functionality, so the user cannot access their device anymore. This type of malware does not encrypt users files; they go one step further and lock the device of the user. The attacker demands a ransom to unlock the device.
- Crypto ransomware – Crypto-ransomware encrypts your important data, such as documents, pictures and videos, but doesn’t interfere with basic computer functions. The purpose of the crypto-ransomware attack is to encrypt users’ data/information
- Locky – Locky ransomware targets files often used by designers, developers, engineers and testers. This malware spreads through the mail in an invoice. If the user opens the invoice form mail, locky begins to encrypt a large array of file types using AES encryption.
- WannaCry – WannaCry was designed to exploit a security vulnerability in Windows. This ransomware targeted over 0.3 million+ computers. The ransomware strain affected Windows machines through a Microsoft exploit.
- Bad Rabbit – Bad Rabbit directs users to install a fake Adobe Flash, thereby infecting the computer with malware. A user could be exposed to the virus simply by visiting a malicious or compromised website and downloading the file they believe to actually be adobe updates.
“Ransomware Attack” Prevention.
It is difficult to prevent a ransomware attack. As we discussed before, various malware spread worldwide. Ransomware can be dangerous for an organisation that does not take precautions. Every organisation should follow the instructions given by their CISO(chief information security officer) for the prevention of ransomware. Some of the points by CISO to help prevent malware.
– Antivirus :
We can use antivirus to defend our system against ransomware. Top-quality antivirus software is highly recommended because Larg well-known companies have already categorised their antivirus based on the structure of malware. High-quality antivirus not only defends but also gives detailed information to user about the detected malware.
– Network Segregation:
Network Segregation is a process that keeps your critical data from access on the web, and it does so by dividing our network into small parts. The benefit is that if any ransomware attack occurs, only a small portion of our data will be corrupted. The range of the attack will be contained to that particular part of our data.
– Regular Backup:
Regular backup is a useful and most basic tactic. With the help of regular backup, we are no longer bound to pay the ransom. If you keep a regular backup of your data, you can easily recover the data that was corrupted during the attack. You can choose to keep the regular backup on your System and also online cloud storage.
– Employee Awareness :
An Employee awareness program should be held monthly for better security performance. This way, every employee will know how to better defend the system against any malware attack. In the employee’s awareness program, employees can share some ideas for system and network improvisation so that organisations can build their base. A team of selected members should be appointed for protecting the system against the sniffing email.
– Device Control :
All devices should be kept up to date. The antivirus program that is installed on the
Devices should be legal and from a trusted source. The antivirus program installed on the devices should reject the installation of applications/software from unknown sources.
IMP NOTE: There is a website run by a Russian organization www.nomoreransom.org.
Most of the decryption tools are available here and you can report malware attacks.
Conclusion
Do not read or open any untrusted email or files, strictly follow the organization malware prevention protocols, keep your data backed up, and keep your device updated.
#Say NO to Cybercrimes.


