
OAuth 2.0 Misconfiguration Leads to Account Takeover
January 3, 2023
All about Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR)
January 10, 2023
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are a standard for representing claims securely between two parties. The claims in a JWT are contained in the payload and are a set of name-value pairs that convey information about an entity, such as the user or system. The claims can be encoded as a JSON object and used in a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure or as the plaintext of a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) structure. When used in a JWS structure, the claims can be digitally signed or integrity protected with a Message Authentication Code (MAC). When used in a JWE structure, the claims can be encrypted for privacy. It should be noted that JSON Web Token misconfiguration leads to account takeover.
JWTs are used for a variety of purposes, including authentication and authorization. They are often used in modern web applications to transmit information between the client and the server securely.
JSON Web Token (JWT)
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is made up of 3 parts.
- Header: The header defines the algorithm that is used to sign the token.
- Payload: The payload contains actual data that need to be transferred or the user’s id/name/number.
- Signature: The Hash of base64 encoded Header + payload to verify its integrity.
An example of JWT:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5ci
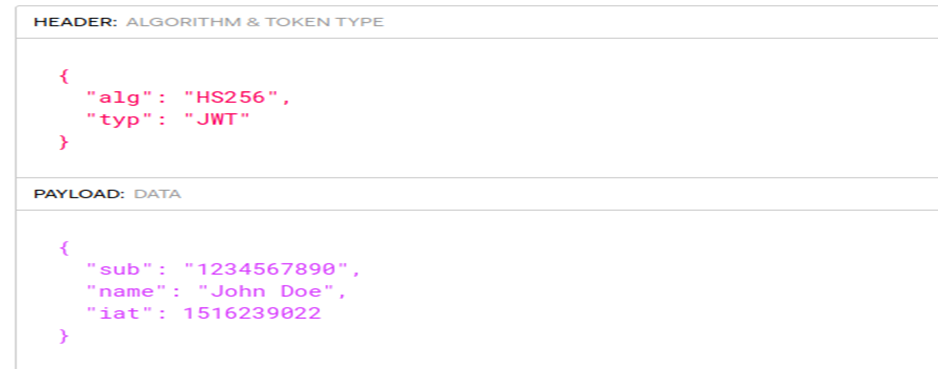
The Header:
The header in JWT will define which algorithm is used while signing the token. It also represents the type of the token, like JWT. It contains other information like a kid and a UUID value; it is used when the server has more than one key to sign the token. So when the server receives the token, it can verify the token’s signature based on the kid parameter to map and verify it with the correct key.
The Payload:
The payload in the JWT is data transferred to the server or used as user identification. For example, user ID, username, some PII, or anything.
The Signature:
SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5ci
In most cases, the payload of a JWT is encoded as a JSON object and is easily readable or modifiable by anyone with access to the token. Therefore, the security of any JWT-based mechanism relies heavily on the cryptographic signature, which verifies the authenticity of the JSON Web Token.
The cryptographic signature is created by signing the JWT with a secret key or by using a public/private key pair. The signature is used to verify that the JWT has not been tampered with and that the claims it contains are genuine. If the signature is invalid, the JWT should be considered untrusted and not used.
The similarity between the Header and Payload:
Both the header and payload in a JSON Web Token (JWT) are JSON objects that contain information about the token.
The header typically contains information about the algorithm used to sign the token and the type of token it is (e.g., JWT).
The payload contains the actual claims or data being transmitted within the token. These claims can include things like the user’s identity, the expiration time of the token, and any other relevant information.
Both the header and payload are encoded as base64 strings and are separated by a period (.) in the token.
One major similarity between the header and payload is that they both contain information that is used to validate the authenticity and integrity of the token. This includes the algorithm used to sign the token and any relevant signature or secret keys.
Overall, the header and payload in a JWT work together to provide a secure and compact way to transmit information between parties.
How to Generate JWT Signature
The server that issues the JWT typically generates the signature by hashing the header and payload of the JWT and using a secret signing key. This process involves using a cryptographic algorithm to create a hash of the header and payload, which is then encrypted using the secret key.
In some cases, the server may also encrypt the resulting hash to add an additional layer of security. Either way, this process helps the server verify whether the token’s data has not been tampered with since it was issued.
- The signature is directly derived from the header and payload of the JWT, and any change to a single byte of the header or payload will result in a mismatched signature. This is because the signature is created using a cryptographic algorithm that is designed to be sensitive to even the smallest changes in the input data.
- Without knowing the server’s secret signing key, generating the correct signature for a given header or payload should not be possible. This is because the secret key encrypts the signature, and only the server that issued the JWT knows the secret key.
Prerequisites
Before diving into JSON Web Token vulnerability and exploiting it, you must set up some tools.
- Use Burp Suite, an all-in-one tool for penetration testing.
- After installing Burp Suite, you need to install an extension called JWT Editor.
What is JSON Web Token Misconfiguration?
Most security vulnerabilities arise due to incorrect implementation by the developer. Sometimes they need to complete the development in a short time, so they have not checked for security in deep, and sometimes, the developer doesn’t know much about security vulnerabilities. An attacker can exploit this misconfiguration to generate or forge the Modifies Access token, which can lead to an Account takeover of any user by manipulating the token.
Who does JSON Web Token Misconfiguration affect?
JWT vulnerability can affect any organization or individual using JWT (JSON Web Token) as an authentication method. It can also potentially affect end users who rely on the security provided by JWT in their interactions with an affected organization or system. Let’s check who does it affect?
- An attacker can take over the victim’s account and compromise the system.
- An attacker gives himself high privileges on the system or an application that is not given to regular users, like admin privileges.
- If the victim has admin-level privileges, it leads to sensitive information disclosure of an organization or gets access to some critical infrastructure of the organization.
How is it being Exploited?
Like every other vulnerability, there are several ways in which a JWT (JSON Web Token) vulnerability can be exploited. Let’s check it out.
1. For example, https://example.com is an application that has register and login functionality.
2. After registering and logging in, the server will assign a Session Token in JSON Web Token Format. You can use the JWT editor Burp Suite extension.
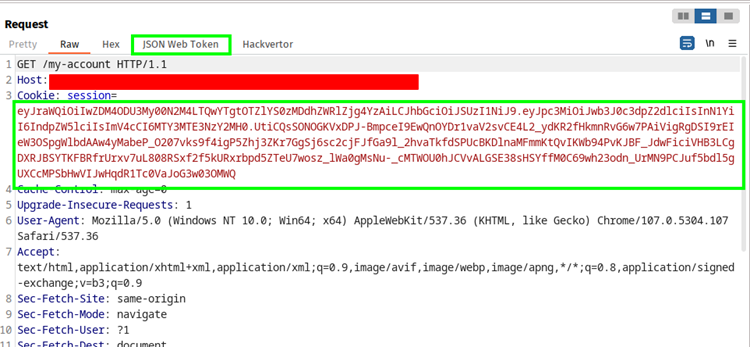
3. Use the JWT editor to inspect and modify the header.
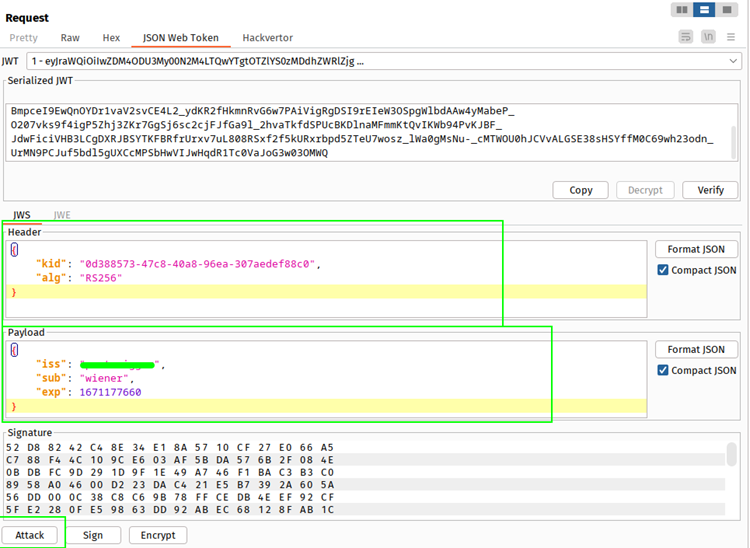
3. You change the payload like here, the sub is the username. Now change that to the victim’s username, like an administrator. Click format JSON, and send it to the server using a repeater.
4. Observe that the server accepts the modified token. But still, you can access that user’s account and do everything on behalf of that user.
5. Since the server does not validate the signature, it only checks whether it is present. But it is not actually computing signature and validating that. You can modify or forge your own token into it and exploit the vulnerability.
Other JWT Misconfiguration
Misconfigurations in JWT tokens are a common problem. These errors occur when the token content is incorrectly set leading to security issues such as unauthorized access to services. The JWT tokens are subject to the following misconfigurations;
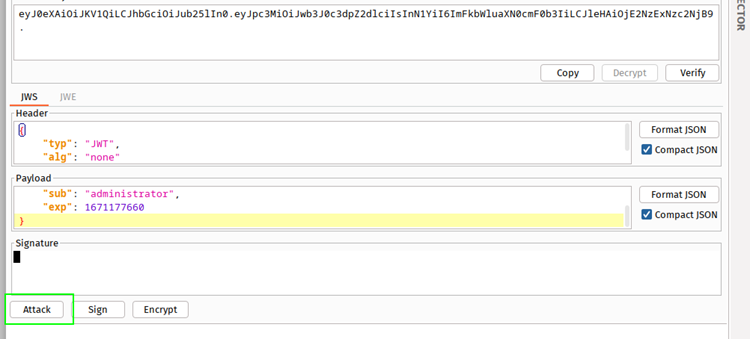
The server has implemented an HS256 algorithm to sign the token, but the server also accepts tokens with a None signature. This means you can modify the payload data and, use the JWT editor Burp extension. Click on the attack, choose none Signature Algorithm, and send the token to the server. You can exploit JSON Web Token misconfiguration with a None signature algorithm attack.
Brute Forcing the secret that is used to sign the token in the HS256 algorithm.
Recommendations to fix the Vulnerability
The JWT vulnerability is present in many platforms and applications, including your company.
The steps below will guide you through the necessary process of fixing this vulnerability in your application.
- Properly verify the signature of the incoming token on the server side.
- Don’t use common secrets in case of using HS256 signing algorithms. Use long secrets that are hard to brute force or guess.
- Implement JSON Web Token properly so the server cannot accept the JWT with no algorithm.
- Use the Up-to-date library for handling JSON Web Token tokens.
- Enable the issuing server to revoke the tokens on log out and after a particular amount of time.
Ensure Security with SecureLayer7
Ensure to test all possible test cases for JSON Web Token misconfiguration, such as Lack of encryption, weak secret key, lack of expiration, lack of validation, lack of rate limiting, Lack of input validation, and lack of proper error handling before implementing the JWTs to avoid vulnerabilities towards these attacks. Hence systems and organizations are safe.
Securelayer7 is a leading penetration testing partner that offers state-of-the-art web apps, mobile apps, and cloud penetration testing to safeguard themselves effectively and their data from existing and emerging cyber tests. Contact us to find out how Securelayer7 can help with testing your JWT tokens.