
The Complete SOC2 Compliance Checklist
December 16, 2022
The importance of Penetration Testing in Banking and Finance
December 28, 2022
A common question that arises with regard to SOC 2 compliance is whether or not penetration testing is required.
While it is not necessary to perform penetration testing to obtain SOC 2 compliance, controls must be in place to detect and prevent unwanted access to systems, apps, and data.
Penetration testing is an excellent technique to evaluate where an organization is vulnerable and find any gaps in its security, even if it is not a requirement for SOC 2. Additionally, it can assist businesses in deciding where to prioritize their cybersecurity efforts.
More importantly, a penetration test can aid in the compliance of regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and GDPR.
Certain organizations, particularly those that handle sensitive customer data, must adhere to certain regulatory requirements. A few of them are:
- PCI-DSS for companies that process transaction data
- SOC 2 Type II for service organizations
- ISO 27001 for any organization requiring information security.
- GDPR for any company with EU customers
- HIPAA for healthcare institutions
However, just because you’re not in one of these industries doesn’t mean that penetration testing isn’t for you. As an organization, safeguarding sensitive information from cyber criminals should be of utmost priority.
SOC 2 TYPE II Penetration Testing Service
Let’s take this from the top.
What is SOC 2 Type II Compliance?

In recent years, the vast majority of organizations have moved their activities to the cloud. This calls for granting some third-party providers access to their cloud infrastructures. In reality, more than 80% of companies have taken this action.
This has two major drawbacks. Although using third-party goods and services makes a company more competitive, they also raise the risk of sensitive data breaches and leaks.
Businesses that offer third parties’ access to their cloud infrastructure must protect sensitive data and strictly adhere to consumer privacy laws. A standardized method of guaranteeing compliance is required due to the differences between enterprises and the cloud services they employ as well as the strict regulation and enforcement of data privacy.
System and Organization Controls for Service Organizations 2 (SOC 2) are essential in this situation.
SOC 2 outlines how businesses should guard against unauthorized access, security breaches, and other risks. Security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy are the five Trust Services Criteria upon which the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) established SOC 2.
SOC reports come in two varieties:
- Type I outlines the systems of a vendor and whether or not their design complies with pertinent trust principles.
- Type II describes how well those systems function operationally.
What Allows an organization to Be SOC 2 Compliant?
There is no formal SOC 2 standards checklist, in contrast to a strict certification process like ISO 27001.
The AICPA Trust Services Criteria instead offers instructions for how to organize each audit. They also provide “points of focus” to assist businesses in putting controls in place.
Examples of how an organization can meet each Trust Services Criteria need are provided in these topics of focus. Here is an illustration from the AICPA’s Trust Services Criteria guide.
The second area of attention on the list talks about having clear-cut standards of behavior that are conveyed to everyone in the company. One example of an organization meeting the standards of CC1.1 is by implementing a code of conduct policy.
However, each company will have to determine whatever controls are necessary to bring its systems into conformity with SOC 2 requirements.
Penetration testing requirements for SOC 2 compliance
Since the TSC serves as the foundation for all SOC 2 criteria, you must comprehend its specifics before starting a formal SOC 2 audit.
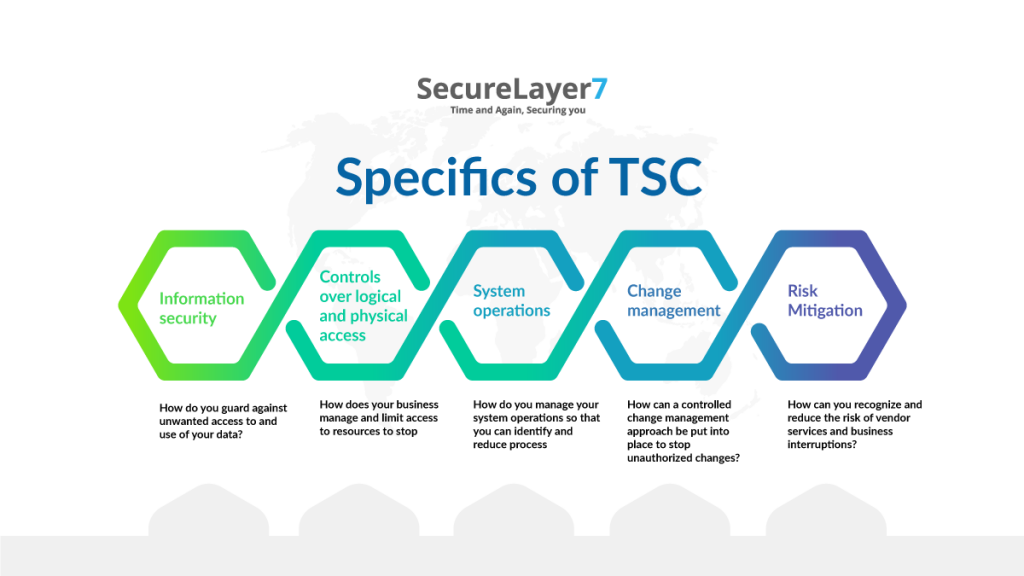
An organization might create multi-factor authentication, set up new staff onboarding procedures, and build systems to prohibit customer data downloads in order to meet the logical and physical access controls criteria.
Another business might limit physical access to data centres, evaluate user access and permissions on a quarterly basis, and keep an eye on production systems.
Again, no particular set of rules or procedures is necessary. What is important is whether the safeguards should be implemented to meet that specific Trust Services Criteria.
Trust Services Principles
Only one of the five Trust Services Principles or Criteria listed below must be mentioned in a SOC 2 report: security. Depending on the overarching objectives of your firm, you can include the other four as optional additions to the audit.
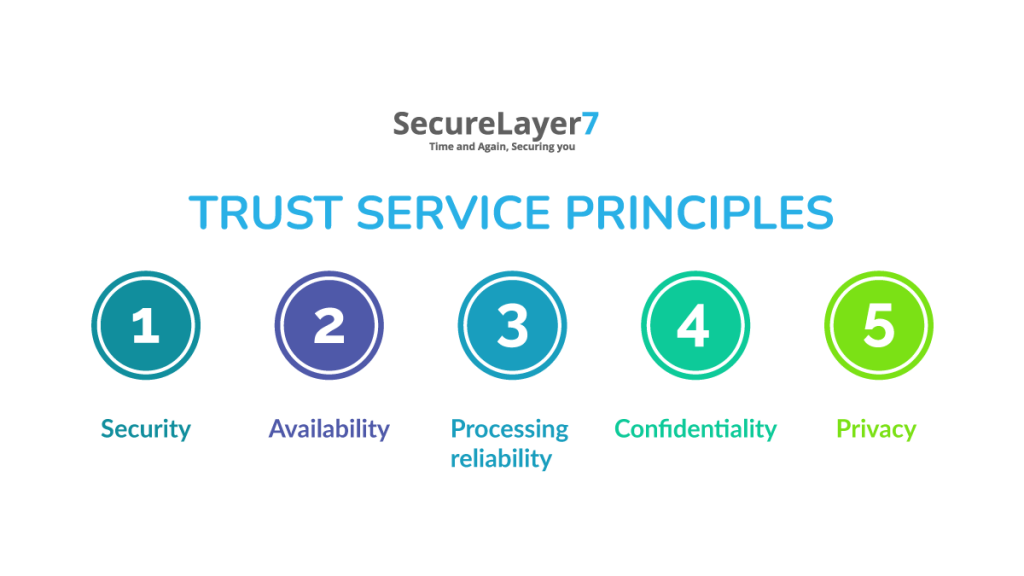
1. Security
Verifying that unwanted access is blocked is the aim of the security audit. The audit will evaluate implemented solutions, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, user authentication protocols, and other things.
On the basis of the findings, suggestions will be made to plug any holes and fix any vulnerabilities.
2. Availability
The audit of availability will examine a few items. For instance, the availability of services, which involves checking the respect for service-level agreements (SLAs) with providers Additionally, network performance has an impact on availability.
Does it regularly function with little downtime for both clients and service providers?
3. Processing Reliability
The processing integrity audit confirms that the system processing has not been affected by any faults. If faults do happen, it looks at whether they are found and fixed right away without impairing services or operations.
It will also check to see if the data is delivered on time and in the appropriate format. For businesses in the financial services industry, this principle is particularly crucial.
4. Confidentiality
This audit verifies that only users with the appropriate permissions can see the data. Additionally, it looks at topics including data classification, encryption, IT mapping, privileged access, and data preservation and disposal.
5. Privacy
Comparable to a confidentiality audit, a privacy audit focuses primarily on the handling and storage of sensitive user data. It investigates whether, when, how, and why a company discloses such data.
Conclusion
Penetration testing is an important part of ensuring compliance with a variety of regulatory frameworks. By identifying and assessing the risks associated with your systems, you can verify that your security controls are adequate and meet the specific requirements of each framework.
Pentests can also provide evidence of due diligence for auditors. When it comes to compliance, it is always advisable to consult an expert penetration testing company specialized in meeting compliance requirements.


