
A Quick Guide To Incident Response Planning
April 7, 2023
Getting Started with Android Pentesting
April 12, 2023
Penetration testing has become a critical component of cybersecurity in recent years, with organizations increasingly recognizing its importance. However, there’s a new debate in the cybersecurity industry: whether to use automated or manual penetration testing.
Many experts argue in favor of automated penetration testing, viewing it as the future of this practice. While automated testing has gained significant traction, manual testing remains an essential tool that shouldn’t be ignored.
In this blog, we’ll explore the debate between automated and manual penetration testing. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to determine which method of penetration testing is best suited to your organization’s needs. We’ll examine the pros and cons of both approaches so that you can make an informed decision.
What is Penetration Testing and Why is it Important?
Penetration testing, also known as pen testing, is a crucial process that simulates a real-world attack on a computer system, network, or application. The aim of this practice is to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious attackers.
Penetration testing has two types: automated and manual.
Automated testing involves the use of software tools to scan and test a system for vulnerabilities. These tools can detect open ports, weak passwords, and known software vulnerabilities. However, automated testing has limitations and cannot identify more complex security flaws that require human intuition and expertise.
Manual testing, on the other hand, involves an expert security professional manually testing a system for vulnerabilities. This can involve a combination of techniques such as social engineering, exploiting application logic flaws, and bypassing access controls. Manual testing is more thorough and can identify more complex vulnerabilities that automated tools may miss.
Penetration testing is essential because it helps organizations identify and remediate security vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. By identifying vulnerabilities, organizations can take steps to patch them, implement better security controls, and reduce the risk of a cyber attack. Additionally, penetration testing is useful for meeting regulatory compliance requirements and demonstrating due diligence in protecting sensitive data.
What is Automated Pentesting?
Automated penetration testing is the process of using software tools to scan and test a computer system, network, or application for security vulnerabilities. These tools simulate attacks that an attacker might carry out to identify vulnerabilities and potential entry points.
Automated pen testing is faster and more cost-effective compared to manual testing, making it a popular choice for many organizations. It helps identify and prioritize high-risk vulnerabilities and provides recommendations for remediation.
Some of the key features of automated pen testing include scanning, vulnerability assessment, exploitation, and reporting.
- Scanning: Automated pen testing tools can scan a system for open ports, services running on those ports, and operating systems and software versions to identify known vulnerabilities and potential entry points.
- Vulnerability assessment: After scanning, the tool performs a vulnerability assessment to categorize identified vulnerabilities by severity, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts.
- Exploitation: In some cases, automated pen testing tools can also exploit identified vulnerabilities to determine the extent to which the system is vulnerable. This phase of automated pen testing can help organizations understand the potential impact of any vulnerability on their systems and networks.
- Reporting: Finally, automated pen testing tools generate detailed reports on the vulnerabilities identified during the testing process. These reports may include recommended remediation steps and other actionable insights.
Advantages Of Automated Pen Testing
Automated penetration testing, or pen-testing, involves using software tools to simulate cyber attacks on a system to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by real attackers.
Here are three advantages of using automated pen-testing.
1. Speed
Automated pen-testing tools can rapidly scan a system and identify potential vulnerabilities much faster than manual testing. This is because the tools can perform tasks such as vulnerability scanning, exploit testing, and reporting in a fraction of the time it would take a human tester to do the same.
As a result, automated pen-testing can be completed in a shorter amount of time, allowing organizations to quickly identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
2. Scalability
Automated pen-testing can be easily scaled to test large or complex systems that would be difficult for manual testing to cover. This is because automated tools can run multiple tests simultaneously, whereas manual testers can only perform one test at a time.
Additionally, automated pen-testing tools can be easily integrated into continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, allowing for automated testing at each stage of the development process.
3. Cost-effectiveness
Automated pen testing can be more cost-effective than manual testing. While manual testing requires skilled testers and can be time-consuming, automated testing tools can be run by IT staff with minimal training.
Additionally, because automated testing can be completed much faster than manual testing, it requires fewer man-hours to complete, which can result in significant cost savings for organizations.
Overall, automated pen-testing can help organizations identify and remediate vulnerabilities in a faster, more scalable, and cost-effective manner than manual testing.
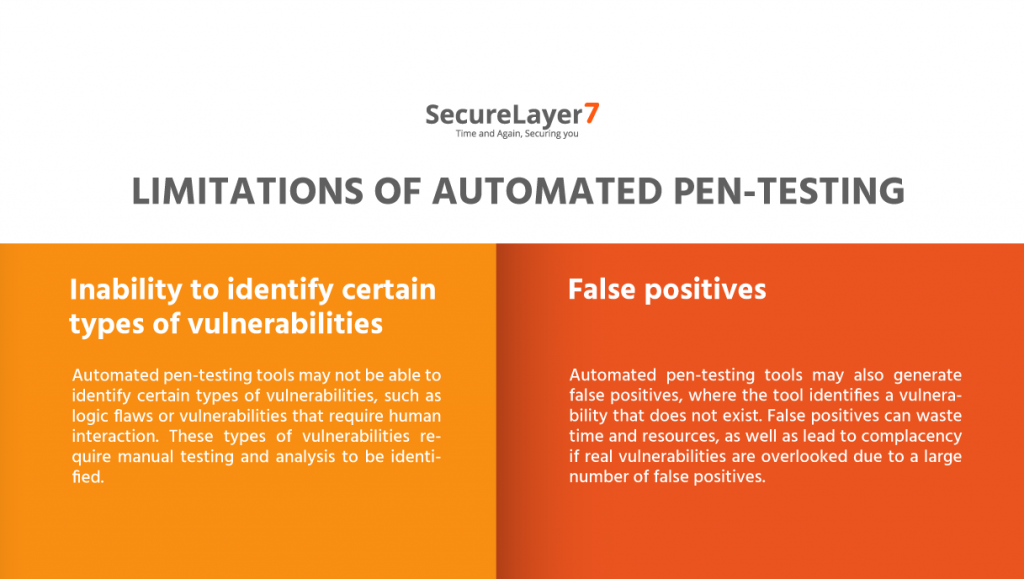
Limitations of automated pen-testing
Automated penetration testing, also known as automated pen-testing, can be an efficient way to identify vulnerabilities in a system or application. However, there are some limitations to automated pen-testing that should be considered.
Popular automated pen-testing tools
There are many automated pen-testing tools available in the market. Some of the popular ones include,

1. Vulnerability scanners
Vulnerability scanner scan a system or application for known vulnerabilities and provide a report of the findings. Examples of popular vulnerability scanners include Nessus, OpenVAS, and Qualys.
2. Network mapping tools
Network mapping tools map out the network topology and identify the devices and systems connected to the network. Examples of popular network mapping tools include Nmap, Fping, and Angry IP Scanner.
3. Exploitation frameworks
Exploitation frameworks automate the process of exploiting vulnerabilities in a system or application. Examples of popular exploitation frameworks include Metasploit and CANVAS.
4. Wireless network scanners
These tools scan wireless networks for vulnerabilities and weaknesses in encryption and authentication protocols. Examples of popular wireless network scanners include Aircrack-ng and Wireshark.
What is Manual Pen Testing?
Manual Penetration Testing (Pen Testing) is a type of security testing performed by human testers, also known as ethical hackers, to identify vulnerabilities in a system or network.
The objective of manual pen testing is to simulate a real-world attack and identify potential weaknesses that an attacker could exploit to gain unauthorized access or steal sensitive information.
Manual Penetration Testing involves the following steps:
- Planning and Reconnaissance: In this step, the pen testers gather information about the target system, including its network infrastructure, operating system, applications, and security controls.
- Scanning: In this step, the pen testers use various tools to scan the target system and identify open ports, services, and vulnerabilities.
- Exploitation: In this step, the pen testers attempt to exploit the vulnerabilities identified in the previous step to gain unauthorized access to the target system.
- Post-exploitation: In this step, the pen testers perform further activities, such as privilege escalation, lateral movement, and data exfiltration, to assess the severity of the vulnerabilities and the impact of a successful attack.
- Reporting: In this step, the pen testers document their findings, including the vulnerabilities identified, the exploits used, and the recommendations for remediation.
Manual Penetration Testing requires a high level of expertise and experience, as it involves complex techniques and tools that must be used carefully to avoid causing any damage to the target system.
The results of manual pen testing can provide valuable insights into the security posture of an organization and help improve its overall security.
Advantages of manual pen-testing
There are several advantages to manual penetration testing, including the following.
1. Ability to Identify Complex Vulnerabilities
Manual penetration testing can identify complex vulnerabilities that automated tools may miss. Human testers can think creatively and find ways to exploit vulnerabilities that an automated tool may not be able to detect.
2. Human Expertise and Intuition
Manual penetration testing involves skilled human testers who can use their expertise and intuition to identify potential security risks that automated tools may not be able to identify.
Human testers can assess the severity of vulnerabilities and understand their impact on the target system or network.
3. Realistic Simulation
Manual penetration testing can simulate real-world attacks by mimicking the actions of an actual attacker. This can provide a more accurate assessment of the security posture of an organization, as it takes into account the full range of techniques that an attacker might use.
4. Customization
Manual penetration testing can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization. Testers can tailor their approach to focus on areas of greatest concern, or to test specific scenarios that may be unique to the organization.
5. Comprehensive Reporting
Manual penetration testing provides detailed reports that document vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation. These reports can be used to improve the overall security posture of the organization, by identifying areas that need improvement and outlining specific steps to address vulnerabilities.
Limitations of manual pentesting
Manual penetration testing, while an important component of a comprehensive security program, does have some limitations.

1. Time-Consuming
Manual penetration testing requires highly skilled professionals who can take significant time to complete the testing process. This can be a drawback for organizations that need to test their systems quickly and efficiently.
2. Higher Cost
The highly specialized skills required for manual penetration testing can be costly, and organizations may need to pay a premium for these services.
3. Risk of Human Error
Manual penetration testing is subject to human error, and even highly skilled testers can make mistakes or overlook vulnerabilities. It’s important to have rigorous quality control measures in place to minimize the risk of errors.
SecureLayer7 has measures in place to mitigate the risk of human error during manual penetration testing. However, even with these measures, there is still a risk that some vulnerabilities may be missed or not fully explored.
That’s why SecureLayer7 has a multi-layered approach to security testing that includes automated testing tools, vulnerability scans, and ongoing monitoring of systems and networks.
Examples of manual pentesting techniques
Here are some examples of manual penetration testing techniques.

1. Social engineering
This technique involves trying to manipulate employees into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise the security of the organization. Social engineering techniques can include phishing emails, pretexting, and baiting.
2. Code review
This technique involves analyzing the source code of an application to identify vulnerabilities that may be present in the code. The code review process may involve manual analysis or the use of automated tools to assist in the review.
3. Red team assessment
This technique involves simulating an attack on an organization’s systems and infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities that may be present. The red team may use a variety of manual techniques to attempt to gain access to the organization’s systems, such as brute force attacks, port scanning, and vulnerability exploitation.
4. Password cracking
This technique involves attempting to crack passwords that are used to access systems or applications. The tester may use a variety of manual techniques, such as dictionary attacks or brute force attacks, to try to crack the password.
5. Application testing
This technique involves testing the security of an application to identify vulnerabilities that may be present. The tester may use manual techniques, such as input validation testing and session management testing, to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Automated Vs Manual Pentesting
Let us make a comparison between Automated and Manual testing at a glance to have a better understanding.
| Manual Testing | Automation Testing |
| Testing performed manually by a human tester | Testing performed automatically using software tools and scripts |
| Requires a human tester to execute test cases and scenarios | Test cases and scenarios are executed automatically by software tools and scripts |
| Useful for exploratory testing, where the tester can explore the software and identify potential issues | Useful for repetitive testing, such as regression testing |
| Requires a higher level of human expertise, intuition, and creativity | Requires expertise in test automation and scripting |
| Effective in situations where the software is complex, the requirements are changing frequently, or the user experience is critical | Effective in situations where the software has a large number of repetitive tasks or is subject to frequent changes |
| Time-consuming and expensive in the long run | Faster execution and turnaround time |
| Provides detailed feedback on the user experience and usability of the software | Limited ability to identify defects related to the user experience or usability |
| Limited scalability and coverage of testing | Improved accuracy and coverage of testing |
| Higher risk of human error and inconsistencies in testing | Consistency and repeatability of test results |
| Suitable for ad hoc and one-time testing | Suitable for long-term and repetitive testing |
| Limited ability to test under high volumes of traffic or user activity | Useful in load testing, where the software is tested under high volumes of traffic or user activity |
While automated penetration testing can be helpful for basic security checks and identifying common vulnerabilities, it has limitations in terms of scope and the ability to identify complex and novel attack vectors.
Manual penetration testing, on the other hand, can provide highly targeted and customized testing, with the ability to identify complex and novel attack vectors.
Manual testing can also provide greater flexibility and adaptability to changing circumstances, and the ability to analyze results in context and provide more in-depth reporting.
While manual testing can be time-consuming and costly, it is the better bet for a comprehensive penetration test because it can identify a wider range of vulnerabilities and provide more detailed reporting.
Additionally, manual testing can be tailored to the specific needs and risks of an organization, making it a more effective way to identify and mitigate security threats.
Conduct comprehensive, manual penetration tests with SecureLayer7
SecureLayer7’s experienced and highly skilled team of penetration testers use a variety of advanced testing methodologies and techniques to identify vulnerabilities in your systems, networks, and applications.
They can simulate real-world attacks, identify exploitable weaknesses, and provide detailed reports that highlight the risks and recommendations for remediation.
With SecureLayer7’s manual penetration testing services, you can gain a deeper understanding of your organization’s security posture and ensure that your critical assets are protected against the latest cyber threats.
By identifying vulnerabilities and providing recommendations for remediation, you can proactively mitigate potential security risks and avoid costly data breaches.
SecureLayer7’s manual penetration testing services are customizable and tailored to meet your specific needs and budget. They are designed to provide a comprehensive and holistic approach to security testing that goes beyond automated tools.
Contact SecureLayer7 to learn more.


