Modern applications rely heavily on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which enable seamless communication between different parts of a software system. For example, developers use the IPStack API to track and identify website visitors.
However, with APIs being used at such a large scale, managing them has become a significant challenge for security teams. Many APIs are unmonitored, unregistered, or unsecured, causing IT security teams to lose track of them.
This problem further compounds the risk. Unmanaged endpoints can expose sensitive data to threat actors and expand an organization’s attack surface.For instance, a 2025 campaign exploited Stripe’s deprecated API to steal credit card details from multiple e-commerce sites, exfiltrating only usable data while evading detection. This incident underscores how technical debt and poor lifecycle management create high-risk vulnerabilities.
In this blog, we will examine shadow API security risks in detail, explore methods for detecting them, and discuss best practices to prevent their proliferation.
What is a Shadow API?
Put simply, shadow APIs refer to undocumented APIs that remain in the system without official oversight or management. They are not found in the documentation or captured in API inventory processes. Since security teams are unaware of their presence, these APIs can bypass established security protocols.
Shadow APIs emerge from various scenarios , such as rushed development, outdated or legacy systems, system migrations, or third-party integrations. They are often created through shadow security practices.
CISOs and business leaders need to address shadow APIs as they increase the risk of data breaches and regulatory non-compliance.
How Shadow APIs Appear in Development
Shadow APIs usually show up because modern teams move fast; sometimes too fast for formal processes to keep up. When a developer needs something quickly, like testing a new feature or grabbing data from a third-party service, spinning up a quick, unofficial API feels harmless.
Though it’s meant to be temporary, it’s just a shortcut to keep things moving. But once it works, everyone moves on, and that little “quick fix” quietly becomes a shadow API.
They also appear when teams aren’t frequently communicating to each other as much as they think they are. Developers might build an internal API for a project, while Ops or security teams build their own version because they didn’t know one already existed.
The duplicates are rarely documented, and nobody takes ownership of them, so they slip into the shadows.
Cloud-native environments make the problem even easier to trigger. Containers, autoscaling, IaC, and CI/CD pipelines create and destroy resources constantly.
New API routes can show up during a deployment or scale-up event, and if nobody updates the central inventory right away, those routes go unnoticed. Before long, an endpoint that appeared automatically or “just for testing” ends up running in production with no tracking and no guardrails.
Difference Between Shadow APIs And Official APIs
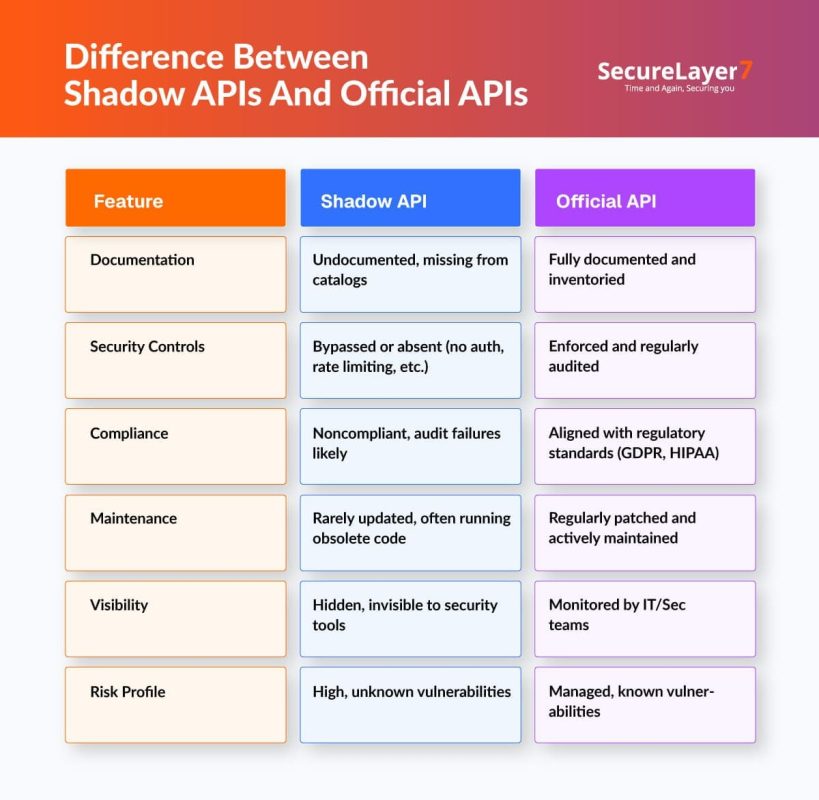
Shadow APIs differ from official APIs in many ways. The fundamental difference is official APIs are properly documented, monitored, and actively maintained:
Documentation
Shadow APIs often appear when teams move fast or experiment without following internal review. Because they skip documentation, nobody except the developer knows what these endpoints do or what data they expose.
In contrast, official APIs follow a structured documentation process. They include details like input/output formats, authentication rules, rate limits, and version notes.
Security Control
Shadow APIs sit outside normal security protections. Without authentication, encryption, or input validation, they become low-hanging fruit for attackers. Since they can miss the radar of monitoring tools, suspicious traffic can slip unnoticed.
On the other hand, official APIs are designed with security in mind from the start. They use modern access control, rate limiting, schema validation, and API gateways to enforce policies.
Compliance
Shadow APIs often violate compliance rules without anyone realizing it. They might process personal data, log sensitive information, or bypass consent flows, yet leave no record of who accessed what. When regulators ask for proof or logs, organizations struggle to respond.
Official APIs support compliance through features like consent management, access logs, and encryption policies. These controls help teams demonstrate responsible data handling for frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
Maintenance
Shadow APIs rarely have a clear owner. Nobody checks them for outdated dependencies, security patches, or performance issues. As they age, minor bugs accumulate to grow into bigger security weaknesses.
On the other hand, official APIs have defined owners and follow a predictable maintenance cycle. They’re patched, updated, versioned, and monitored to ensure reliability. This keeps performance strong and reduces long-term risk.
Visibility
Shadow APIs often operate in the dark. They don’t send logs to observability tools or analytics platforms, making it almost impossible to spot unusual behavior. If data goes missing or traffic spikes, there’s no easy way to investigate.
Official APIs are visible in dashboards, gateways, and monitoring tools. Logs, metrics, and alerts help security teams catch anomalies early, troubleshoot faster.
Risk Profile
Shadow APIs expand the attack surface with unsecured, unknown endpoints. They enable data exfiltration, lateral movement, and breaches without detection.
In contrast, official APIs present managed risks, protected by layered defenses, continuous testing, and incident response, minimizing exploitation chances.
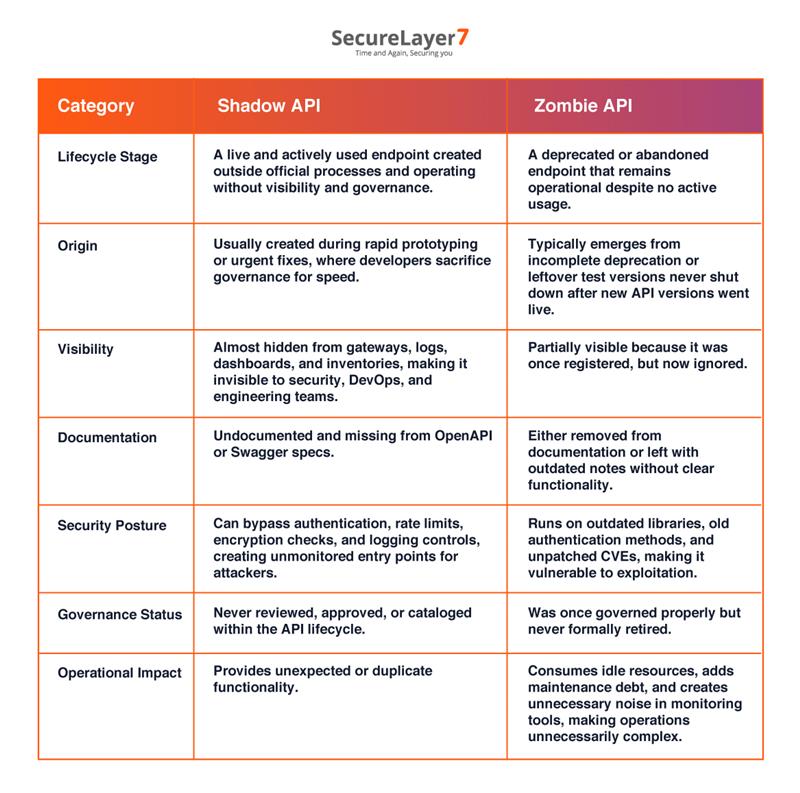
Zombie APIs vs Shadow APIs: What’s the Difference?
A zombie API is an old, or abandoned APIs that is not actively maintained by developers, but they are still operational. Most organizations inadvertently create zombie APIs when they fail to retire old APIs once their purpose is solved. The risk with zombie APIs is that they remain accessible despite not being used and can be exploited by hackers.
Impact on Business and Brand
Shadow API risks go beyond financial risks. They can inflict lasting damage to an organization’s brand reputation. Breaches caused by unmanaged shadow APIs can lead to a loss of trust and loyalty in the brand. In addition, the operational inefficiencies stemming from shadow APIs can drain resources.
In 2025, the average cost of a data breach dipped slightly to around $4.44 million, down from $4.48 million. That sounds like progress, but it leaves out huge factors like lawsuits and long-term reputation damage. The only reason the number dropped at all is because companies are getting faster at detecting and containing attacks.But that advantage disappears completely with shadow APIs.
Shadow APIs are invisible by nature—no monitoring, no alerts, no logging; so you often don’t even know where the breach started. Tracking it down quickly is almost impossible. Remember the T-Mobile breach? It was sitting quietly in their systems for 40 days before anyone noticed.
Real-World Examples of Shadow API
These real-world examples show how simple misconfigurations or overlooked controls can open serious security gaps:
Example #1: Microsoft Azure API Management Data Exposure
A misconfiguration in Azure’s API Management service exposed internal endpoints due to permissive default policy settings. Many organizations left backend service APIs accessible because inbound policy rules weren’t properly defined.
Example#2: GitLab API Rate Limit Bypass
GitLab’s API had a vulnerability that allowed brute-force attacks through weak rate limiting. Exploiting the users endpoint, attackers bypassed the throttling mechanism to enumerate user accounts.
These incidents remind us that even well-documented APIs can become entry points if they’re misconfigured or insufficiently monitored.
How to Identify Shadow APIs
Managing shadow APIs is critical for mitigating security risks. Below, we outline how to effectively detect these hidden APIs:
Common Warning Signs of Shadow APIs
Though identifying shadow APIs is not easy, there are certain warning signals that indicate their presence. Some common signs include:
- Unrecognized API Traffic: Unusual API traffic patterns, such as spikes or traffic from unknown sources, may indicate the existence of shadow APIs.
- Undocumented Endpoints: APIs without proper documentation or that are not included in the API inventory are most likely shadow APIs. Such situations often occur when developers use APIs to address immediate needs without following formal processes.
- Anomalous Response Times: Unexpected delays in the response time can indicate unauthorized or unmonitored API calls.
- Resource Allocation Spikes: Sudden increases in resource usage may indicate the presence of undocumented APIs. These APIs could be responsible for consuming more resources than expected.
Tools and Technologies for Shadow API Detection
There are several open source and paid tools that can help organizations detect shadow APIs effectively:
Open Source API Discovery Tools
Several automated tools, such as Google Apigee’s Shadow API Discovery, can assist in scanning for existing undetected and undocumented APIs related security vulnerabilities. These tools can help in analyzing traffic patterns and provide detailed insights into potential shadow APIs without affecting performance.
Here is a list of some open source tools:
- OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy) can intercept API traffic and identify undocumented APIs. It also performs basic security testing, making it a valuable tool for discovering and auditing shadow APIs.
- Fiddler is a web debugging proxy that intercepts, modifies, and analyzes API traffic. It captures all HTTP and HTTPS traffic, making it particularly useful for locating such APIs on the client side.
- Mitmproxy is a free, open-source interactive HTTPS proxy. It allows you to inspect, modify, and replay API requests, making it an excellent tool for uncovering hidden APIs.
Log Analysis Solutions
Using powerful logging tools can help monitor the API usage closely. It can analyze logs for unusual activities, allowing security teams to detect suspicious transactions.
Outbound Proxy Monitoring
Outbound proxies are used to intercept all outgoing API calls and capture detailed logs of requests and responses. This enables security teams to identify and spot unrecognized transactions by analyzing unusual patterns.
Shadow API Detection Methods
Effective discovery of shadow APIs requires using a combination of methods:
Scan Codebases Regularly
Before going into production, it’s imperative to regularly identify undocumented APIs. This can be accomplished by scanning various codebases or application environments.
Monitor Log Activities
One of the most popularly used methods to identify and detect shadow APIs is log analysis. It enables security teams to monitor real-time application logs to identify newly developed endpoints and unusual API metrics. This method allows for immediate detection of API issues and facilitates rapid remediation.
Using open source tools, such as Loggagent can assist in this process by providing insights into API usage patterns and anomalies.
Conduct Networks Audit
Using network scanning tools can help identify hidden API endpoints that may otherwise remain undetected. This falls outside the scope of established protocols.
Best Practices for Shadow API Prevention
Mitigating the associated risks of shadow APIs is an essential component of modern cybersecurity practices. Research shows shadow APIs account for up to 50% of enterprise API traffic, yet remain invisible to security teams. The following practices can help your organization in this effort.
1. Establish API Governance Policies
Organizations seeking to protect against shadow API-related data breaches can start by establishing proper API governance policies and guidelines for development and usage. Several studies show organizations with formalized API governance experience 70% fewer shadow API incidents.
- Introduce a standardized process for deploying new APIs. Define clear stages for development, review, testing, and production release.
- Enforce approval workflows involving security and architecture teams.
- Require registration with the IT and/or security team. Use a centralized portal or API gateway for onboarding. Ensure every API is vetted for security and compliance before going live.
- Mandate comprehensive API documentation. Include endpoints, parameters, authentication methods, rate limits, and example requests.
- Keep documentation updated with each API version change.
- Implement an API management framework to view all APIs in one place and create a single source of truth across your organization.
2. Implement API Security Standards and Protocols
Data breaches involving APIs often stem from security misconfigurations. It is important to ensure that basic security best practices are in place for all your APIs:
- Implement a strong password security mechanism. Enforce minimum length, complexity, and rotation policies. Use secure hashing algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2 for password storage.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA). Use identity providers like Okta, Azure AD, or Auth0 that support MFA.
- Authenticate via at least two factors—such as a password and a time-based one-time code—before granting API access.
- Enforce reasonable token expiration times. Set short-lived access tokens and use refresh tokens with strict validation.
- Rotate and invalidate tokens automatically upon expiration or suspicious activity.
- Adopt the principle of least privilege. Assign users and services only the minimum permissions necessary. Automated enforcement of these controls is more effective than manual oversight alone.
- Shift security left by building OpenAPI contract checks and policy enforcement directly into your CI/CD pipelines, so issues surface early instead of after deployment.
- Add contract testing, such as schema diffs or drift blockers—to your CI workflow to keep APIs consistent and stop undocumented changes from slipping into production.
- Use graph-based correlation to spot shadow endpoints that are exposed externally, handle sensitive data, or sit on high-risk pathways in your architecture.
3. Implement Proper Monitoring and Logging
Real-time API monitoring and continuous discovery is vital for establishing baseline usage and detecting suspicious activities. Organizations with mature monitoring detect security incidents 3–5× faster than those relying on manual reviews.
- Monitor suspicious activities, such as APIs called from unusual locations or at odd hours.
- Use UEBA tools to establish normal behavior baselines.
- Implement comprehensive logging to track all API calls and usage.
- Capture request headers, response codes, IP addresses, and timestamps. Include user identity and endpoint details for full context.
- Maintain logs for compliance requirements and audit purposes.
- Store logs in encrypted, immutable storage and apply retention policies aligned with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Enable developers and security personnel to debug issues and investigate incidents. Forward logs to SIEM or observability platforms.
- Ensure role-based access control (RBAC) and fast search capabilities for timely analysis.
4. Integrate Continuous API Discovery into CI/CD Pipelines
- Automate discovery scans during every build to catch undocumented or shadow APIs before they reach production.
- Run automated security checks on any newly found APIs to prevent vulnerable versions from being released.
- Keep your findings synced with API inventories and monitoring tools to maintain consistent governance and real-time visibility across environments.
Deploy API Gateways
- Use API gateways as the universal entry point instead of applying runtime security controls in isolation that leads to gaps and inconsistencies.
- Centralize monitoring, logging, and analytics at the gateway to identify APIs missing security controls, policy coverage, or compliance alignment.
- Enforce schema validation and unified authentication/authorization at the gateway—such as OIDC or OAuth scopes.
Embed API security into DevSecOps workflows
- Integrate API security into existing DevSecOps practices rather than adding friction or manual checks.
- Add API security scanners so that the code is always checked before it gets deployed.
- Automate API documentation, tagging, and encryption to keep inventories accurate.
Track And Monitor Key KPIs
CISOs must track the following metrics to measure shadow API discovery effectiveness:
- The number of undocumented endpoints detected periodically
- Shadow API Coverage Ratio that is % total APIs inventoried vs. discovered
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD): Hours from deployment to identification
- API Traffic Anomalies Flagged: Daily unusual endpoint calls caught
- Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR): Days from detection to secure/deprecate
- Inventory Completeness Score: % APIs with owners, docs, and controls.
Shadow API Risk Maturity Model
Now, the question arises from where to start. It is essential for CISOs and engineering teams to know where they stand right now. That’s where the shadow API risk maturity model comes into picture.
Put simply, Shadow API Risk Maturity Model is a framework that helps organizations evaluate how well they identify, manage, and eliminate shadow APIs.
Level 0: Unaware
- It’s a phase when engineering teams operate without an API inventory.
- Shadow APIs remain entirely invisible, often discovered only after an incident.
- Logging, gateway routing, and documentation are inconsistent or missing.
Level 1: Reactive
- Teams identify Shadow APIs only when performance issues or breaches occur.
- Discovery relies on manual inspection, tribal knowledge, and developer escalation.
- No policies exist for registration or approval.
Level 2: Emerging
- In this phase, basic API cataloging starts and traffic analysis tools detect some unmanaged endpoints.
- Teams are aware of the presence of shadow APIs, but enforcement is weak.
Level 3: Managed
- Security scans validate authentication, encryption, and logging.
- Shadow API discovery becomes periodic and technology-assisted, reducing unmanaged endpoints significantly.
- A central API inventory, versioning rules, and registration policies are implemented. .
Level 4: Proactive
- Automated discovery continuously monitors deployments, gateways, and traffic patterns.
- Developers mandatorily register APIs before deployment.
- Security policies apply uniformly, and unauthorized endpoints are blocked or quarantined.
Level 5: Optimized
- Continuous mapping, automated remediation, and governance dashboards ensure near-zero unmanaged APIs.
- Organizational culture prioritizes visibility, lifecycle hygiene, and secure-by-default development.
Key Capabilities to Consider While Selecting a Shadow API Detection Tool
Choosing the right shadow API detection tool isn’t just about features;it’s about staying ahead of hidden risks. You need to consider various capabilities like visibility, accuracy, and seamless integration across your entire tech stack:
Real-time Traffic Visibility
The API discovery tool must monitor all API traffic cross cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments. Immediate detection of unknown endpoints is essential. Therefore, look for low-latency analysis that flags anomalies like unusual payloads or access spikes. This ensures threats are caught as they emerge.
Automated API Discovery
The shadow API detection tool should find APIs without relying on documentation or gateways. Using traffic sniffing, behavioral analysis, and machine learning can help detect undocumented, forgotten, or rogue endpoints. This includes internal microservices, mobile app APIs, and legacy systems operating outside governance.
Contextual Metadata Enrichment
Each discovered API should come with rich context. Know the source, owner, data sensitivity, and usage patterns. This helps security teams prioritize risks. Developers can trace endpoints back to code, enabling faster remediation and better accountability.
Outbound Traffic Interception
Many shadow APIs call external services directly. The tool must intercept outbound traffic. Proxy-based monitoring or agent-based collection captures these calls. This reveals third-party integrations and SaaS usage that bypass internal controls.
CI/CD Integration
Prevention starts early. The API scanner tool should plug into CI/CD pipelines and Infrastructure-as-Code workflows. It scans code and configuration files before deployment. This stops undocumented APIs from reaching production. Automated discovery at build time reduces blind spots.
Dynamic Risk Validation
Not every discovered API is a real threat. The best tools assess exposure. They check if an endpoint is internet-facing or handles sensitive data. Some simulate attack paths. This reduces false positives. Teams focus only on exploitable risks.
For example, a tool like Google Apigee or BugDazz API Security Scanner can make a real difference.
They work across runtime, network, and development stages, not just spotting hidden APIs but helping teams understand and secure them.
It’s this layered visibility spanning discovery, context, and control that minimizes risk over time.
Conclusion
On a final note, shadow APIs present a significant risk to security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Organizations can manage these challenges by raising API security awareness within the development team and implementing strict policies. They should also employ tools for API discovery and incorporate automation into their processes. Additionally, monitoring and targeted security assessments can play a critical role in maintaining a secure API environment.
Take control of your API security! SecureLayer7 offers tailored solutions to combat shadow APIs and protect your data. Contact us now.
FAQs on Shadow APIs
Outbound proxies monitor all outgoing API calls, capturing requests and responses to identify undocumented endpoints. They automatically catalog APIs in use, though they can add latency or become bottlenecks if not properly scaled.
Analyzing API logs provides real-time insight into traffic patterns, revealing unknown or newly created endpoints. Anomalies in usage, response codes, or payloads help security teams spot suspicious activity early.
Yes. Integrating API discovery into CI/CD pipelines scans code during builds, catching undocumented APIs before deployment. This ensures only approved, secure APIs make it into production.
Shadow API detection tools fall into several categories:
• API discovery and inventory tools that scan code and networks to find undocumented endpoints
• Outbound proxies and API gateways that log outgoing API calls;
• Log analysis tools that spot anomalies in traffic;
• CI/CD integration tools that scan code during builds;
• Network traffic analysis tools that detect unusual API activity at the network level.
Shift-left integrates API discovery and testing into CI/CD pipelines, detecting undocumented endpoints during development. This ensures only registered, secure APIs reach production, reducing reliance on post-deployment fixes.



