For years, penetration testing worked because IT infrastructure was relatively static. Applications changed slowly, infrastructure was predictable, and conducting pentesting a few times a year gave a reasonable degree of confidence.
However, this assumption no longer holds. Cloud-native environments evolve continuously. New APIs are deployed and retired quietly. The attack surface now shifts faster than any scheduled test can track. At the same time, attackers aren’t waiting for quarterly windows. They can pounce on any opportunity for exploitation. They use automation and AI to discover, chain, and exploit weaknesses as they appear.
This creates a chasm between how environments operate and how offensive security is traditionally implemented. That’s the gap autonomous pentesting is designed to plug.
In this blog, we’ll explain autonomous pentesting, how it works, and why CISOs are embracing it and its use cases.
Understanding Autonomous Pentesting
Autonomous pentesting refers to a process where penetration testing runs in the autopilot mode and doesn’t wait for a scheduled security audit or a human-led exercise. It uses AI to plan reconnaissance and launch attacks, learn from results, and adjust its approach with minimum or no human involvement at every step.
Instead, it runs continuously in the background and behaves like a real attacker. It looks at applications, APIs, cloud setups, and running systems, then actively tries to break in safely to see what’s actually exploitable. It thinks more like an actual attacker exploring an unfamiliar environment.
On the other hand, traditional automated pentests help, but they mostly follow a scripted path. Autonomous systems can do it better. They look at how identities, configurations, and services connect together. And, based on the analysis, they can build attack chains to exploit vulnerabilities across cloud setups, internal networks, and APIs.
This is why teams working in DevSecOps love it as autonomous testing keeps up with the pace of development. Every change can be retested automatically, giving engineers quick, reliable feedback instead of waiting weeks for a manual assessment.
How Autonomous Pentesting Works: Step-by-Step Lifecycle
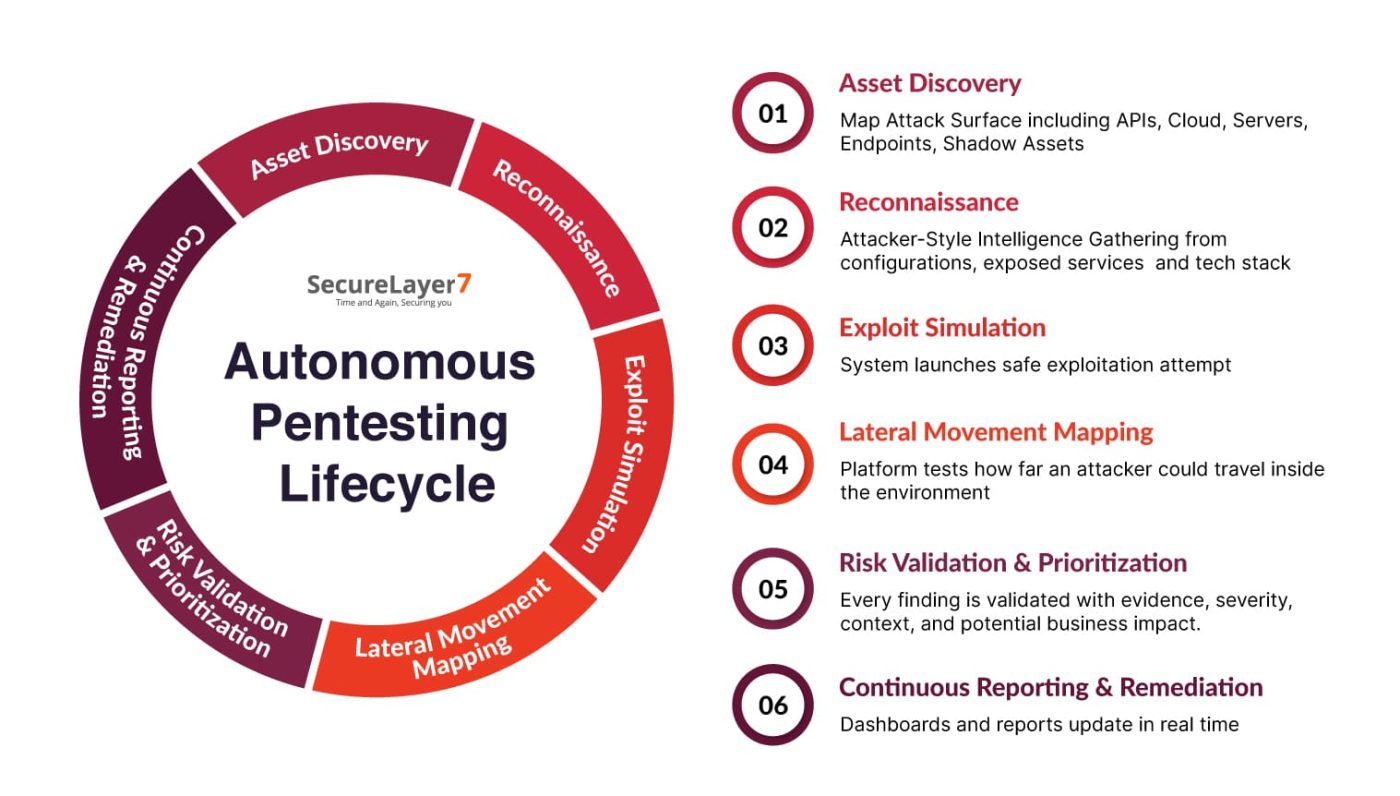
Here is how autonomous pentesting works step by step:
1. Asset Discovery: Autonomous pentesting starts with identifying assets in the environment that includes APIs, servers, cloud configurations, API endpoints, and shadow microservices. It helps create an accurate map of your attack surface.
2. Reconnaissance: AI agents collect configuration details, exposed services, technology stacks, and potential weak points. This reconnaissance mirrors how real attackers prepare, giving the platform enough intelligence to craft precise and context-aware attack paths.
3. Exploit Simulation: Once security vulnerabilities are identified, the autonomous pentesting system launches safe exploit attempts designed to mimic genuine adversary techniques. It focuses on confirming real vulnerabilities rather than flagging false-positives and improving the accuracy of results.
4. Lateral Movement Mapping: If an exploit succeeds, the platform tests how far an attacker could travel inside the environment using threat simulation. It identifies chained vulnerabilities, privilege gaps, and pivot points that reveal the true blast radius of a compromise.
5. Risk Validation & Prioritization: Every finding is validated with evidence, severity context, and potential business impact. This cuts out false positives and helps security teams prioritize what needs immediate attention versus what can be scheduled.
6. Continuous Reporting & Remediation Guidance: Dashboards and reports update in real time, offering clear explanations, recommended fixes, and trend insights. The system automatically restarts its cycle, maintaining continuous coverage as the environment evolves.
Why Autonomous Pentesting Matters
The most significant benefit of autonomous pentesting is that it removes the guesswork from security testing, while saving time. Instead of waiting weeks or months for the next review, you get continuous visibility into what’s exposed and what’s changed. That means security vulnerabilities are identified as they surface, and can be fixed faster before hackers exploit them.
Autonomous penetration testing becomes all the more important in a cloud environment where APIs are everywhere and they frequently change. Apart from an organization’s own APIs, the environment may contain third-party APIs, and vendors of these third-party APIs. New endpoints may get added, and RBAC permissions keep evolving.
Autonomous pentesting helps by continuously discovering APIs, studying logs, including internal, forgotten, and shadow endpoints that usually don’t show up in official inventories. It validates whether tokens can be reused, roles can be escalated, or trust between services can be abused. This becomes critical in microservices-heavy setups where a single opening can quietly open doors to many others.
As a result, it releases the workload on security teams by reducing dependence on costly, point-in-time pentests and fewer manual cycles to manage. Security becomes an ongoing process and far more agile.
How Autonomous Pentesting Fosters True Autonomy in Offensive Security
True autonomy in offensive security is about thinking, adapting, and validating like a real attacker would and that’s where AI changes the game. AI-powered reconnaissance lets security platforms observe the security environment the way a real attacker would quietly, patiently, and with context. Instead of merely ticking through a checklist of rules, AI looks at how systems are actually wired together.
It notices exposed services, configuration, attack paths, and technology fingerprints. Based on the evaluation, it builds a threat simulation of how access might realistically unfold. It drives better decisions.
Apart from pointing out weaknesses, it selects which methodology to use next, while linking attack steps based on what works and what doesn’t. When it fails, it doesn’t give up or blindly repeat the same move. It adapts fast and changes tactics, explores nearby paths, and tests alternate routes, similar to a human attacker. That ability to adjust in real time is what turns simple automation into true autonomy for security teams.
Additionally, autonomous pentesting doesn’t raise alarms for every possible misconfiguration. It carefully tests whether a security issue can actually be exploited, using safe, controlled techniques. As a result, there are fewer false positives.
Where Autonomous Pentesting Delivers the Business Value
Autonomous pentesting, powered by AI, is most effective in modern environments where systems change frequently, attack paths are interconnected:
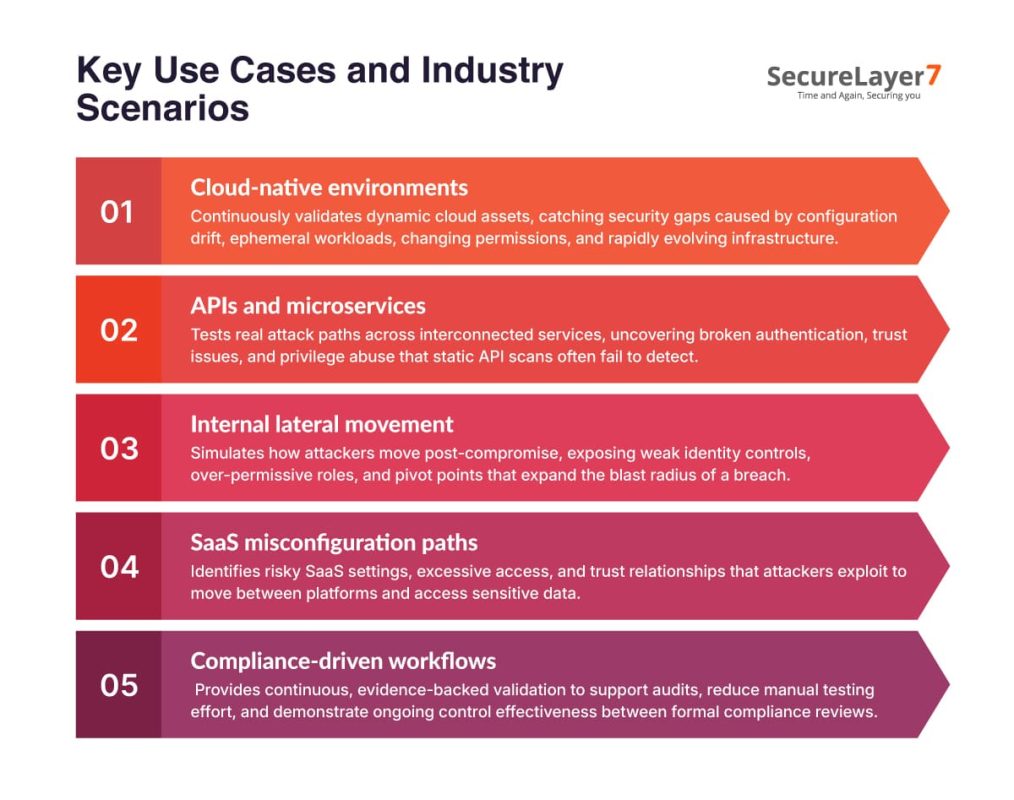
- Cloud-native environments: Continuously validates dynamically evolving cloud assets, while detecting security gaps from configuration changes, and rapidly evolving infrastructure environments.
- APIs and microservices: Tests real attack paths across interconnected services, identifying broken authentication, trust failures, and privilege abuse that static API scans usually miss.
- Internal lateral movement: Simulates attacker movement after compromise, revealing weak identity controls, excessive permissions, and pivot points expanding breach impact across enterprise environments.
- SaaS misconfiguration paths: Identifies dangerous SaaS configurations, excessive access rights, and trust relationships attackers exploit to traverse platforms, exposing sensitive data assets broadly.
- Compliance-driven workflows: Delivers continuous evidence-backed validation supporting audits, reducing manual testing, and proving ongoing control effectiveness between reviews across regulated enterprise environments.
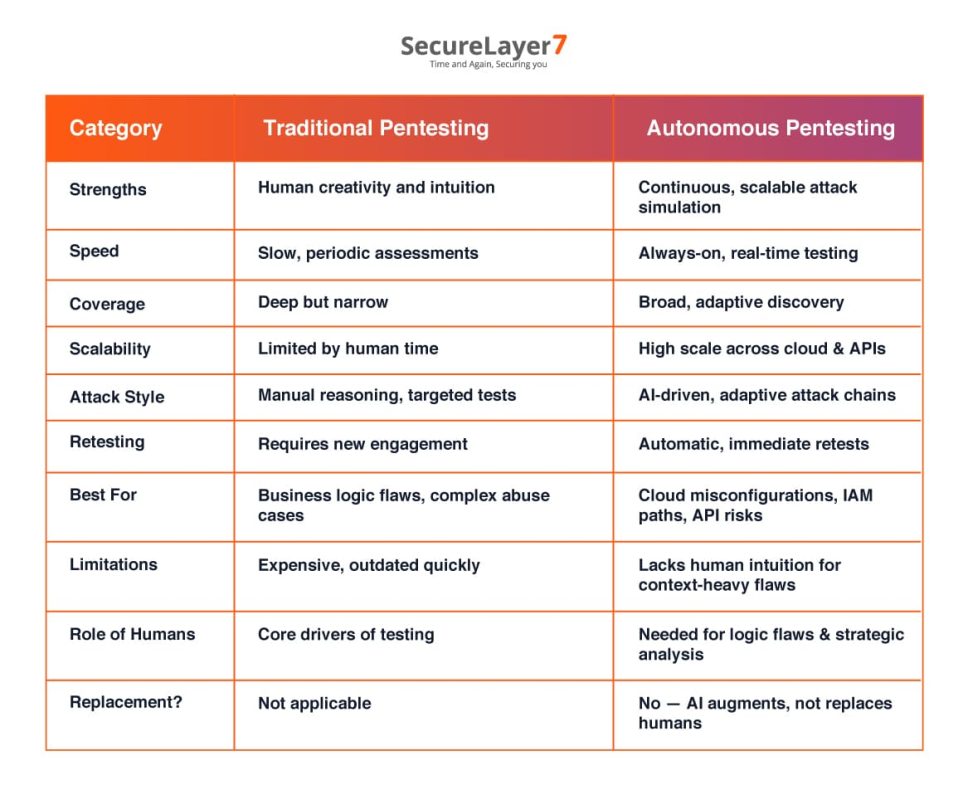
Autonomous Pentesting vs. Traditional Pentesting: Key Differences
Traditional pentesting leverages human insights, but can’t keep up with the fast-changing security environment. Some of the key differences between autonomous pentesting and traditional pentesting are as follows:
Can Autonomous Pentesting Replace Human Testers? A Realistic Perspective
People often ask whether autonomous pentesting will replace human testers. In reality, that’s not the right way to look at it. What really changes is how the work between the two gets divided.
Autonomous pentesting is very good at the repetitive, time-consuming parts of testing. It can keep retesting the same environments as they change, view cloud assets quickly, and cover a lot more ground than a human team ever could. Every new release, configuration tweak, or identity change can be checked again automatically, without planning cycles or long gaps between tests. It does the heavy lifting.
Human testers still bring something that machines don’t. They think sideways. They notice odd behaviors, broken workflows, and logic flaws that don’t show up in standard checks. A good tester can look at how a system is supposed to work and can figure out quickly how it can be exploited by hackers. That kind of judgment and creativity is hard to automate.
The future of offensive security sits somewhere in the middle. Autonomous systems handle the continuous checking and heavy lifting, while human testers focus on deeper, high-risk scenarios and novel attack ideas. Together, they create a more realistic and effective security approach than either could alone.
Limitations of Autonomous Penetration Testing
Autonomous pentesting brings speed and scale, but it doesn’t replace human judgment. Some areas of offensive security rely deeply on context, creativity, and responsibility. These are the spaces where human testers continue to play a critical role:
- Business logic testing: Logic flaws often hide in how features are meant to work, not in how they’re coded. Humans understand intent, workflows, and edge cases, allowing them to spot abuse scenarios that automated systems typically miss.
- Social engineering and human trust exploitation: Attacks involving deception, persuasion, and timing depend on human behavior. Understanding tone, organizational culture, and emotional triggers requires empathy and judgment that machines can’t reliably replicate.
- Context-driven risk interpretation: Not every vulnerability carries the same risk in every environment. Human testers can weigh technical findings against business impact, operational constraints, and risk tolerance to guide smarter decisions.
- Ethical oversight and decision-making: Humans can define boundaries for testing, they can decide how far simulations should go, and ensure activities remain lawful, responsible, aligned with organizational values.
AI-driven Autonomous Pentesting: How Safe Is It for Your Organization?
The idea of an AI system actively testing defenses can sound risky, especially in live environments. In practice, safety is not an afterthought. It’s integrated into how these systems operate.
Testing is carefully controlled so it doesn’t overwhelm applications or underlying infrastructure. Exploits are executed in sandboxed conditions, enough to confirm a real weakness without introducing risk or disruption.
This is often limited to defined environments, ensuring production systems stay within agreed boundaries. In mature programs, these controls are reviewed and formally approved by security and platform teams before testing begins.
Furthermore, autonomous testing is designed to work quietly in the background. It avoids actions that can harm the security environment, respects rate limits, and adapts its pace based on system behavior. If an application starts showing signs of stress, testing can slow down or pause automatically. This is especially important in regulated industries where uptime and stability are non-negotiable.
Autonomous systems follow strict rules around what data they access, store, and report. Sensitive information is masked, logs are controlled, and findings align with internal governance policies.
When done right, autonomous security testing fits seamlessly into existing security, privacy, and compliance frameworks, providing teams the confidence that testing improves security without introducing new risk.
Continuous Security With Autonomous Pentesting: A Practical Enterprise Roadmap
Here are some practical tips for enterprises to integrate autonomous pentesting in their existing security environment:
- Move from periodic pentests to continuous validation: Shift away from annual or quarterly pentests to autonomous continuous penetration testing that continuously validates real exploit paths as environments, code, and identities change.
- Define a focused, risk-driven scope: Start with internet-facing applications, APIs, cloud workloads, and identity paths that matter most for the system’s security, then expand coverage gradually.
- Configure safe testing guardrails: Establish clear boundaries for exploit attempts to ensure production safety, control testing depth, and prevent disruption.
- Set an intelligent testing cadence: Run continuously in the background, with higher frequency triggered by deployments, configuration changes, or IAM updates instead of relying on scheduled testing windows.
- Deliver actionable reporting, not noise: Prioritize findings based on exploitability and business impact, include evidence, and provide clear remediation guidance so teams know exactly what to fix and why.
- Integrate with security governance programs: Feed validated findings into risk registers, compliance workflows, and board reporting, positioning autonomous pentesting as a continuous control alongside human-led testing.
Future of Autonomous Penetration Testing
The future of autonomous penetration testing will largely depend on how fast enterprise security environments evolve. A recent report by Gartner highlights a growing need to incorporate Continuous Threat Exposure Management in vulnerability management.
The report further highlights a clear move away from point-in-time testing toward continuous security validation, largely driven by cloud growth and API sprawl. Several industry data points in the same direction. Autonomous systems are also evolving in what they test. Instead of flagging isolated vulnerabilities, they’re starting to map full attack paths. That distinction matters as real attackers don’t stop after exploiting just a single weakness.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report found that 80% of breaches involve multiple techniques wired together sequentially, such as identity abuse, misconfigurations, and lateral movement, all working in tandem.
According to Deloitte’s Global Future of Cyber Survey, “ cyberleaders worldwide are increasingly embedding advanced technologies, including AI, into their security strategies, signaling broader adoption of automation into core security practices.”
But that doesn’t mean humans will be eliminated from the process. It will remain a critical part of the equation. Autonomous platforms do the heavy lifting that involves increasing scale, repetition, constant retesting, while human testers focus on more critical tasks, such as business logic, edge cases, and making judgment calls where machines still struggle with.
In addition, there is also a growing convergence with governance and compliance. Continuous evidence-driven testing makes it easier to prove controls are working throughout the year, not just with point-in-time offensive security testing.
Practically, autonomous penetration testing doesn’t sideline humans, it enhances their impact.
Why CISOs Are Moving to Autonomous Pentesting for Continuous Security Assurance
Getting reliable and accurate real-time visibility into how their environments can actually be compromised is a big worry for organizations. That’s why CISOs are turning to autonomous pentesting because it helps them address this issue: .
- C-suite executives seek clear answers about the security risks.
- Auditors expect evidence backed by continuous monitoring.
- Leadership teams need a clear way to measure attack exposure without waiting for long for the next manual assessment.
Autonomous pentesting helps CISOs meet these expectations of different stakeholders by providing a steady stream of validated attack data. Continuous validation also changes the nature of security operations.
Instead of reacting to findings long after they appear, teams can spot issues as soon as they surface and respond before attackers exploit them. This moves organizations from a reactive posture to a genuinely proactive one.
At the same time, evolving regulations and cyber insurance requirements increasingly emphasize ongoing testing, not annual check-the-box exercises. Autonomous pentesting naturally aligns with these expectations, providing CISOs a near real-time updated view of the organization’s security posture.
Conclusion
Autonomous pentesting works best when it complements human expertise rather than trying to replace it. By continuously validating real attack paths, autonomous AI testing platforms bring speed, consistency, and scale to the offensive security process. They retest environments as applications, cloud assets, and identities change, helping teams stay ahead of exposure instead of reacting after the fact.
However, human testers remain essential for creativity, business logic analysis, and ethical oversight in the process. Autonomous pentesting removes much of the repetitive and time-bound work. The result is a stronger, more focused security function.
FAQ on Autonomous Pentesting
It reduces exposure gaps between audits by continuously validating risk as cloud assets, APIs, and identities change.
Yes, when properly configured. Testing runs within approved guardrails, using rate limits and sandboxed exploits to avoid disruption.
It creates continuous, evidence-backed proof of security controls instead of one-time reports. This helps teams stay audit-ready and demonstrate ongoing risk management.



